3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(12):2224-2235. doi:10.7150/jca.85650 This issue Cite
Research Paper
KMU-191 Induces Apoptosis in Human Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Caki Cells Through Modulation of Bcl-xL, Mcl-1 (L), c-FLIP (L), and p53 Proteins
1. Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, 1095 Dalgubeol-daero, Daegu 42601, Republic of Korea.
2. Institute of medical science, Keimyung University, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, 1095 Dalgubeol-daero, Daegu 42601, Republic of Korea.
3. Institute for Cancer Research, Keimyung University, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, 1095 Dalgubeol-daero, Daegu 42601, Republic of Korea,
4. R&D Center for Advanced Pharmaceuticals & Evaluation, Korea Institute of Toxicology, Daejeon 34114, Korea.
5. Department of Physiology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon 16419, Korea.
6. Department of Chemistry, Keimyung University, 1095 Dalgubeol-daero, Daegu 42601, Republic of Korea.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
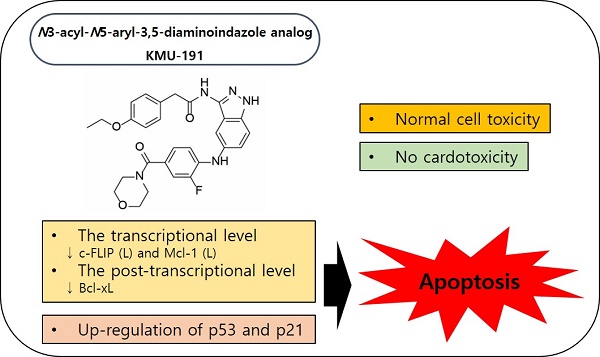
The anti-proliferative effects of a newly developed N3-acyl-N5-aryl-3,5-diaminoindazole analog, KMU-191, have been previously evaluated in various cancer cells. However, the detailed anti-cancer molecular mechanisms of KMU-191 remain unknown. In this study, we investigated anti-cancer mechanisms by which KMU-191 regulates apoptosis-related genes in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma Caki cells. KMU-191 induced poly ADP-ribose polymerase cleavage and caspase-dependent apoptosis. In addition, KMU-191 induced down-regulation of the long form of cellular FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme inhibitory protein (c-FLIP (L)) at the transcriptional level as well as that of long form of myeloid cell leukemia (Mcl-1 (L)) and B-cell lymphoma-extra large at the post-transcriptional level. Furthermore, KMU-191-induced apoptosis was closely associated with the Mcl-1 (L) down-regulation, but also partially associated with c-FLIP (L) down-regulation. In contrast, KMU-191 up-regulated p53, which is closely related to KMU-191-induced apoptosis. Although KMU-191 showed cytotoxicity of normal cells, it unusually did not induce cardiotoxicity. Taken together, these results suggest that a multi-target small molecule, N3-acyl-N5-aryl-3,5-diaminoindazole analog, KMU-191 is a potential anti-cancer agent that does not induce cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: KMU-191, Bcl-xL, Mcl-1 (L), c-FLIP (L), p53, Apoptosis, Renal cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact