3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(1):79-89. doi:10.7150/jca.88668 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Role of heat shock protein 70 in silibinin-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer
1. Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710061, P.R. China.
2. Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710061, P.R. China.
3. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710061, P.R. China.
*Contributed equally.
Abstract
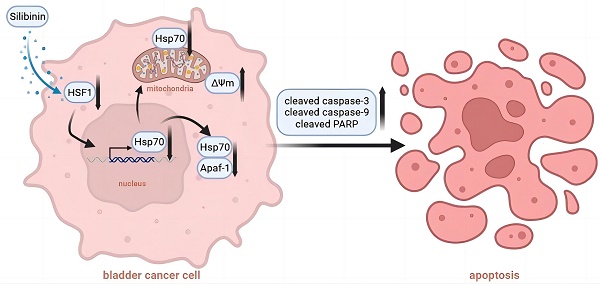
Hsp70 (heat shock protein 70) plays critical roles in cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Recently, accumulating evidences have demonstrated the cancer promoting effects of Hsp70 in bladder cancer. The development of novel therapeutic approaches targeting Hsp70 thus received great attention from researchers. In this study, we demonstrated that silibinin, a natural polyphenolic flavonoid isolated from the milk thistle, targeted Hsp70 by inhibiting its transcription in bladder cancer cells. We also demonstrated that knockdown of endogenous Hsp70 enhanced silibinin-induced apoptosis, while overexpression of exogenous Hsp70 could partially reverse the effects of silibinin-induced cell apoptosis. Furthermore, we found that silibinin could activate HSF1/Hsp70-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Mechanically, silibinin inhibited the interaction between Apaf-1 and Hsp70, thus increasing the recruitment of pro caspase-9. Results from in vivo study demonstrated that silibinin suppressed the growth of bladder cancer xenografts, which was accompanied with the activation of caspase-3 and downregulation of HSF1 and Hsp70. Taken together, our data indicates that silibinin induces mitochondrial apoptosis via inhibiting HSF1/Hsp70 pathway and also suggests the therapeutic potential of silibinin in the treatment of bladder cancer.
Keywords: apoptosis, bladder cancer, HSF1, Hsp70, silibinin

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact