3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(1):204-217. doi:10.7150/jca.89750 This issue Cite
Review
Periprostatic Adipose Tissue: A New Perspective for Diagnosing and Treating Prostate Cancer
1. Department of Urology II, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Pathobiology, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
Abstract
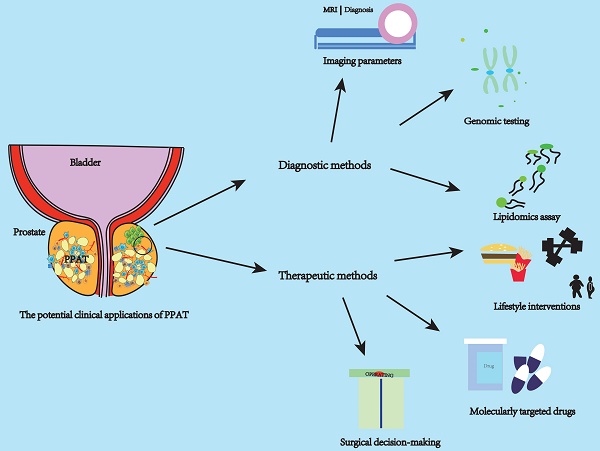
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common tumor of the male genitourinary system. It will eventually progress to fatal metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, for which treatment options are limited. Adipose tissues are distributed in various parts of the body. They have different morphological structures and functional characteristics and are associated with the development of various tumors. Periprostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) is the closest white visceral adipose tissue to the prostate and is part of the PCa tumor microenvironment. Studies have shown that PPAT is involved in PCa development, progression, invasion, and metastasis through the secretion of multiple active molecules. Factors such as obesity, diet, exercise, and organochlorine pesticides can affect the development of PCa indirectly or directly through PPAT. Based on the mechanism of PPAT's involvement in regulating PCa, this review summarized various diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for PCa with potential applications to assess the progression of patients' disease and improve clinical outcomes.
Keywords: prostate cancer, periprostatic adipose tissue, lipids, inflammation, diagnosis, and treatment

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact