3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(2):466-472. doi:10.7150/jca.90525 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Lymph Node Ratio Enhances Predictive Value for Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study
1. Department of Thoracic surgery, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, Guangxi 530021, P.R. China.
2. Department of Radiation Oncology, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, Guangxi 530021, P.R. China.
Abstract
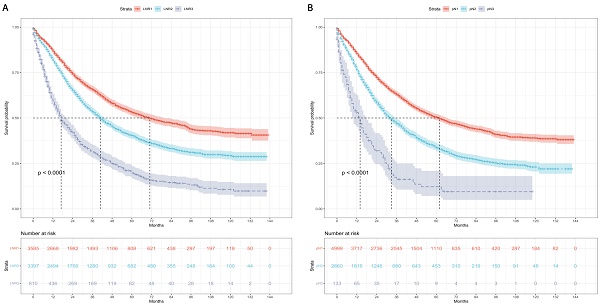
Purpose: To compare the prognostic value of lymph node ratio (LNR) and pN in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) undergoing surgery.
Materials and methods: NSCLC patients were investigated between 2004 and 2015 from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results databases. The X-tile software was used to determine LNR cut-off values. Kaplan-Meier analysis was employed to assess cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: The identified cut-off values of LNR were 0.19 and 0.73. Median CSS for LNR1 (LNR < 0.19), LNR2 (0.19 ≤ LNR ≤ 0.73), and LNR3 (LNR > 0.73) were 71, 41, and 17 months. Both LNR2 (HR = 1.46, 95% CI: 1.36-1.57; P < 0.001) and LNR3 (HR = 2.85, 95% CI: 2.58-3.15; P < 0.001) demonstrated poorer median CSS compared to LNR1. Similarly, median OS for LNR1, LNR2, and LNR3 were 50, 35, and 16 months. LNR2 (HR = 1.36, 95% CI: 1.27-1.45; P < 0.001) and LNR3 (HR = 2.60, 95% CI: 2.37-2.85; P < 0.001) exhibited worse median OS compared to LNR1. A revised pN (r-pN) classification incorporating LNR and pN demonstrated superior penalized goodness-of-fit and discriminative ability in predicting CSS and OS compared to both LNR and pN.
Conclusion: LNR outperformed pN in predicting CSS and OS in NSCLC patients undergoing surgery, potentially leading to more precise adjuvant treatment decisions.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, surgery, lymph node ratio, survival.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact