3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(5):1314-1327. doi:10.7150/jca.88038 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Potential mechanisms underlying inhibition of xenograft lung cancer models by kaempferol: modulation of gut microbiota in activating immune cell function
1. Department of Oncology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China.
2. Shanghai Geriatric Institute of Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work and shared the first authorship.
Abstract
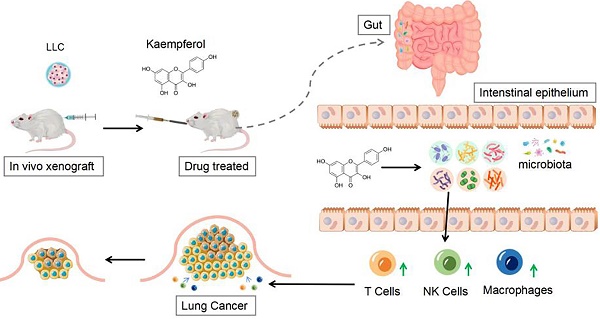
Context: As a flavonoid compound, kaempferol has great potential in anti-lung cancer therapy, but the mechanism of its therapeutic effect needs further exploration.
Objective: To explore the therapeutic effect of kaempferol on lung cancer, as well as its capability to regulate the gut microbiota and stimulate immune function.
Materials & methods: Twenty-four BALB/c mice were divided into four groups. The first two groups, consisting of 12 normal mice, were administered either PBS or Kaempferol (Kaem) via gavage. The remaining 12 mice, which were subcutaneously inoculated with Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) cells, were similarly divided and subjected to the same treatments respectively. The inhibitory effect of kaempferol on xenograft lung cancer models was explored with in vivo experiments, the diversity of gut microbiota was investigated by 16S rDNA sequencing, and the treatment effect on immune cells was quantified using flow cytometry.
Results: Kaempferol exerted a significant inhibitory effect on xenograft lung cancer models in vivo. It effectively inhibited the proliferation of LLC cells and significantly activated cytotoxic T cells, natural killer cells, and other immune cells in mice. 16S rRNA sequencing of fecal samples from tumor-bearing mice treated with kaempferol showed a significant increase in the abundances of potentially advantageous microbial species such as c_Bacilli, o_Lactobacillales, f_Lachnospiraceae, s_uncultured_bacterium_g_Lactobacillus, g_Lactobacillus, f_Bacteroidaceae, g_Bacteroides, and s_uncultured_bacterium_g_Bacteroides, s_Bacteroides_acidifaciens. An increase in the proportions of three types of immune cells might associated with the above dominant bacterial species.
Conclusion: Kaempferol can inhibit xenograft lung cancer models. Such inhibition effect might come from the activation of T cells, NK cells, and other immune cells which are modulated by the gut microbiota.
Keywords: kaempferol, lung cancer, gut microbiota, immunity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact