3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(11):3313-3320. doi:10.7150/jca.95159 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Peripheral Blood Inflammatory Markers as A Reliable Predictor of Gastric Mucosal Metaplasia Change in the Middle-aged Population
1. Department of Management Information Systems, National Pingtung University of Science and Technology, Pingtung, Taiwan.
2. Department of Information and Management, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
3. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Linkou Medical Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
4. College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
5. Healthcare center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
6. Division of cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan Branch, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
7. Department of General Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Taoyuan City, Taiwan.
Abstract
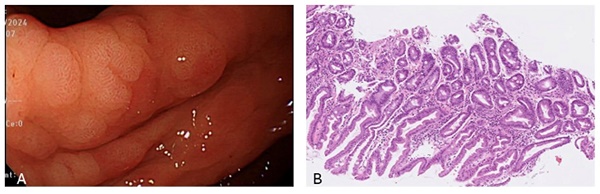
Purpose: The study aims to evaluate the efficacy of peripheral blood inflammatory markers as clinical predictors for gastric intestinal metaplasia (IM), a known precursor to gastric cancer. This research investigates the potential of these markers to serve as reliable indicators for detecting gastric IM.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on 59,143 individuals who underwent checkups at the Taoyuan Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Health Clinic Center from 2010 to 2014. Of these, 11,355 subjects who received gastroscopic biopsies were recruited. After omitting cases with incomplete blood data, the sample was narrowed to 10,380 participants. After exclusion and propensity score matching, subjects in the group with IM and control patients without IM were balanced and included in the study. These subjects were stratified by gender and age, and predictors such as the Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII), and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) were evaluated. Multivariate logistic regression models were employed to analyze the presence or absence of IM accurately.
Results: Out of the 10,380 subjects, 2,088 (20.1%) were diagnosed with IM, while 8,292 (79.9%) did not have IM. In our analysis, inflammation indices were found to have a limited impact on younger patients. For middle-aged and elderly individuals, SII showed statistical significance for predicting IM in males (p=0.0019), while SIRI and MLR were significant for females (SIRI p=0.0001, MLR p=0.0009). Additionally, the Area Under the Curve (AUC) value indicated that inflammation indices were more influential in females (55.1%) than males.
Conclusions: The study results reveal that peripheral blood inflammatory markers could be useful in predicting gastric mucosal metaplasia changes, particularly in middle-aged and elderly populations. Although the markers' predictive power varies with gender, they represent a significant step forward in the non-invasive detection of gastric IM. This could aid in the early identification and management of precancerous conditions.
Keywords: intestinal metaplasia, Systemic Inflammation Response Index, Systemic Immune Inflammation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact