3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(10):3024-3033. doi:10.7150/jca.94539 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Neoadjuvant targeted immunotherapy followed by surgical resection versus upfront surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A multicenter study
1. Department of Liver Surgery, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, PUMC and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Dongcheng, Beijing 100730, China.
2. 4+4 Medical Doctor Program, PUMC and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Dongcheng, Beijing 100730, China.
3. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the 302nd Hospital of Chinese PLA, Fengtai, Beijing, 100039, China.
4. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Jiangxi Provincial Cancer Hospital, Nanchang, Jiangxi, 330029, China.
5. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, 050011, China.
*Xiangan Wu, Yuxin Wang, Sen Wang and Ye Chen contributed equally to this manuscript.
Abstract
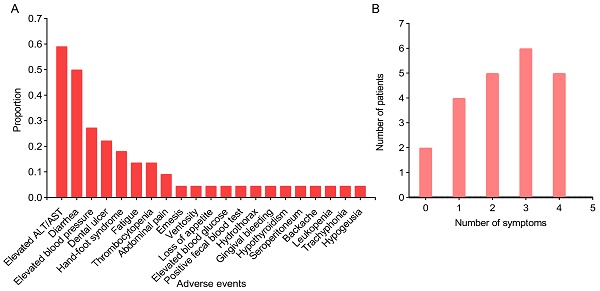
Background: This study aimed to investigate the safety and efficacy of preoperative targeted immunotherapy followed by surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with macrovascular invasion.
Method: Clinical information of HCC patients with macrovascular invasion was collected from four medical centers. These patients were divided into two cohorts: the upfront surgery group (n=40) and the neoadjuvant group (n=22). Comparisons between the two groups were made with appropriate statistical methods.
Results: HCC Patients with macrovascular invasion in the neoadjuvant group were associated with increased incidence of postoperative ascites (72.73% vs. 37.5%, P=0.008), but shorter postoperative hospital stay (10 days vs. 14 days, P=0.032). Furthermore, targeted immunotherapy followed by surgical resection significantly reduced the postoperative recurrence rate at both 3 months and 1 year (9% versus 28.9%, 32.1% versus 67.9%, respectively; P=0.018), but increased the postoperative nononcologic mortality rate within 1 year (20.1% vs. 2.8%; P= 0.036).
Conclusion: For HCC patients with macrovascular invasion, preoperative targeted immunotherapy significantly decreased the postoperative tumor recurrence rate while maintaining relative safety, but such a treatment may also result in chronic liver damage and increased risk of nononcologic mortality.
Keywords: targeted immunotherapy, surgery, complications, the recurrence rate

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact