3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(9):2505-2517. doi:10.7150/jca.90819 This issue Cite
Research Paper
B7-H3 suppresses CD8+ T cell immunologic function through reprogramming glycolytic metabolism
State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan, China; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan, China.
*Wu and Han contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
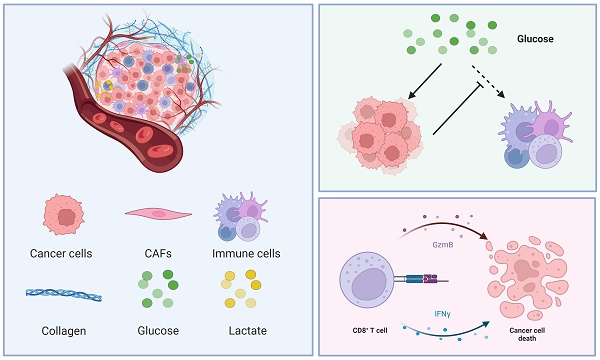
Malignant neoplasms pose a formidable threat to human well-being. Prior studies have documented the extensive expression of B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3 or CD276) across various tumors, affecting glucose metabolism. Yet, the link between metabolic modulation and immune responses remains largely unexplored. Our study reveals a significant association between B7-H3 expression and advanced tumor stages, lymph node metastasis, and tumor location in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). We further elucidate B7-H3's role in mediating glucose competition between cancer cells and CD8+ T cells. Through co-culturing tumor cells with flow cytometry-sorted CD8+ T cells, we measured glucose uptake and lactate secretion in both cell types. Additionally, we assessed interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) release and the immune and exhaustion status of CD8+ T cells. Our findings indicate that B7-H3 enhances glycolysis in OSCC and malignant melanoma, while simultaneously inhibiting CD8+ T cell glycolysis. Silencing B7-H3 led to increased IFN-γ secretion in co-cultures, highlighting its significant role in modulating CD8+ T cell functions within the tumor microenvironment and its impact on tumorigenicity. We also demonstrate that glycolysis inhibition can be mitigated by exogenous glucose supplementation. Mechanistically, our study suggests B7-H3's influence on metabolism might be mediated through the phosphoinositide3-kinase (PI3K)/ protein kinase B (Akt)/ mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. This research unveils how B7-H3 affects immune functions via metabolic reprogramming.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact