3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2020; 11(24):7253-7263. doi:10.7150/jca.50835 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis induces apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma through ROS-regulated mitochondrial pathway
1. School of Dentistry, College of Oral Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
2. School of Oral Hygiene, College of Oral Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
3. Graduate Institute of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Science, Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
4. Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
Abstract
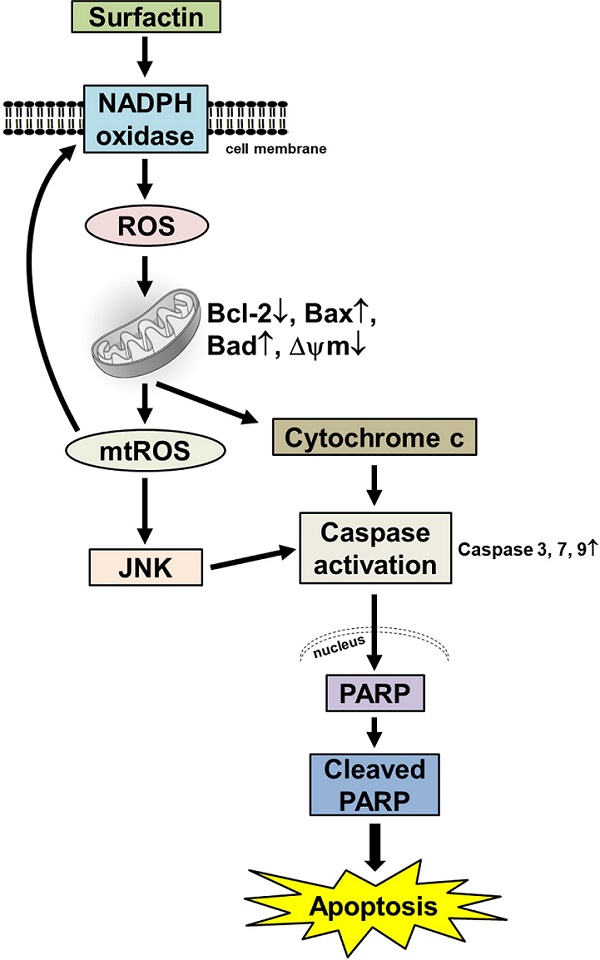
Recently, ambient air particulate matter (PM) has been shown to increase the risk of oral cancer. The most common malignant tumor in the oral cavity is oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Recent studies have revealed that surfactin, a cyclic lipopeptide generated by Bacillus subtilis, has anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. However, the exact anti-cancer effects of surfactin on human OSCC and underlying molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown. In the present study, we found that treatment of SCC4 and SCC25 cells (human OSCC cell lines) with surfactin reduced the viability of SCC4 and SCC25 cells by induction of apoptosis. Surfactin-induced apoptosis was associated with caspase activation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage and was regulated by the mitochondrial pathway, exemplified by mitochondrial depolarization, mitochondrial-derived reactive oxidative species (ROS) production, cytochrome c release, up-regulation of Bad and Bax, and down-regulation of Bcl-2. Surfactin induced NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation, which appeared essential for the activation of the mitochondrial pathway. Surfactin-induced mitochondrial-derived ROS generation was associated with JNK1/2 activation. After treatment with surfactin, ROS caused JNK1/2-dependent cell death of SCC4 and SCC25 cells. Taken together, our findings suggest that surfactin induces mitochondria associated apoptosis of human OSCC cell lines, and surfactin may be a potential chemotherapeutic agent for future OSCC treatment.
Keywords: apoptosis, surfactin, particulate matter, oral squamous cell carcinoma, reactive oxidative species

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact