3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(5):1284-1294. doi:10.7150/jca.51346 This issue Cite
Review
The Role of Tumor Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310009.
2. Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Tumor of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310009.
3. Research Center of Diagnosis and Treatment Technology for Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310009.
4. Clinical Medicine Innovation Center of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310009.
5. Clinical Research Center of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310009.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
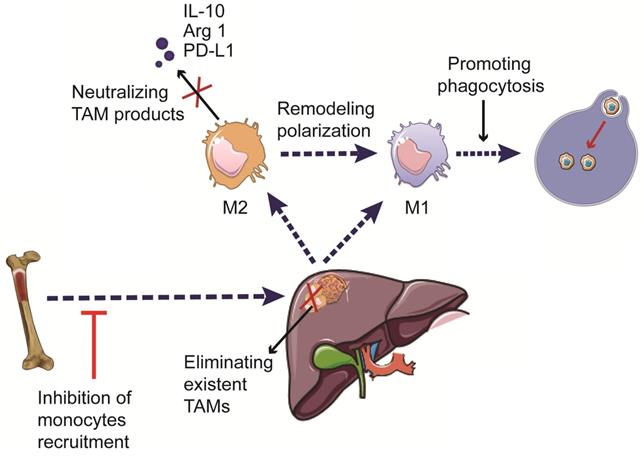
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide and represents a classic paradigm of inflammation-related cancer. Various inflammation-related risk factors jointly contribute to the development of chronic inflammation in the liver. Chronic inflammation, in turn, leads to continuous cycles of destruction-regeneration in the liver, contributing to HCC development and progression. Tumor associated macrophages are abundant in the tumor microenvironment of HCC, promoting chronic inflammation and HCC progression. Hence, better understanding of the mechanism by which tumor associated macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of HCC would allow for the development of novel macrophage-targeting immunotherapies. This review summarizes the current knowledge regarding the mechanisms by which macrophages promote HCC development and progression, as well as information from ongoing therapies and clinical trials assessing the efficacy of macrophage-modulating therapies in HCC patients.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Tumor associated macrophage, Tumor microenvironment, Immunotherapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact