3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(5):1474-1482. doi:10.7150/jca.51593 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Practical Model is Equivalent to the BALAD or BALAD-2 Score in Predicting Long-term Survival after Hepatectomy in Chinese Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Division of Clinical Research, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
2. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
3. Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
Yahui Liu and Jing Jiang. Both authors make an equal contribution to this article.
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the predictive value of the BALAD and BALAD-2 scores on long-term survival after hepatectomy in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients and to attempt to establish a more practical or effective model.
Methods: A total of 251 HCC patients underwent hepatectomy were recruited. The BALAD and BALAD-2 scores were calculated with total bilirubin, albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin. The associations of the two scores and their components with the overall survival were analyzed. Finally, three prediction models were explored and constructed.
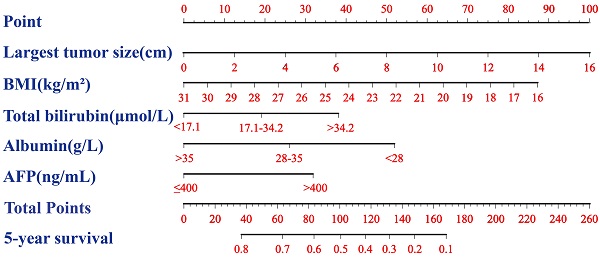
Results: We observed that HCC patients had 5-year survival rates that worsened with increasement of BALAD and BALAD-2 scores. The BALAD and BALAD-2 scores demonstrated fine value in predicting overall survival with Harrell-C statistics of 0.665 (0.618-0.712) and 0.603 (0.554-0.636). After two variables, largest tumor size and BMI, were included in BALAD [0.720 (0.671-0.769)] or BALAD-2 [0.701 (0.649-0.751)] multivariate models, the Harrell-C statistic increased significantly than BALAD (P=0.048) or BALAD-2 (P<0.001) alone. Taking into account availability and expense, an equivalent BAA-BS model was established based on total bilirubin, albumin, AFP, BMI and largest tumor size. The Harrell-C statistic of BAA-BS model [0.723(0.674-0.772)] was similar to that of BALAD (P=0.820) or BALAD-2 (P=0.209) multivariate model. And, the continuous net reclassification index and integrated discriminatory improvement were not statistically different. Finally, a nomogram of the equivalent BAA-BS model was constructed to assist surgeons and patients in predicting 5-year survival rates.
Conclusion: Both BALAD and BALAD-2 scores were highly suitable for predicting long-term survival after hepatectomy in Chinese HCC patients. A significant increase in predictive efficacy was observed after the addition of largest tumor size and BMI to BALAD or BALAD-2 score. Even if AFP-L3 and DCP are not detected, an equivalent BAA-BS model also obtained an excellent discriminatory performance.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Hepatectomy, Survival, BALAD, BALAD-2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact