3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(6):1616-1622. doi:10.7150/jca.52165 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The correlation between tumor size, lymph node status, distant metastases and mortality in rectal cancer patients without neoadjuvant therapy
1. Department of Colorectal Surgery, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 200032, China.
2. Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
# Equal contributions
Abstract
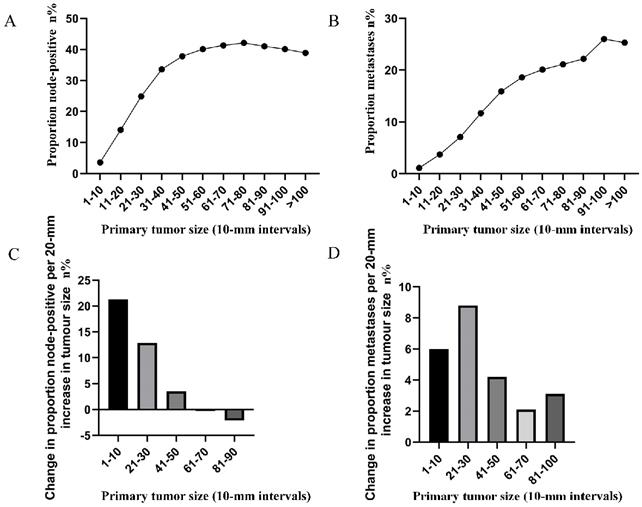
Tumor size has an effect on decision making for the treatment rectal cancer. Transanal local excision can be selected to remove rectal cancer with favorable histopathological features. It is generally recognized that the risk of lymph node involvement and distant metastases increases as the tumor enlarges. However, the majority of the studies classified patients into two groups using concrete value as a cutoff point. The coarse classification was not sufficient to reveal a correlation between the tumor size and lymph node status or distant metastases across the full range of sizes examined. Between 1988 and 2015, a total of 77,746 patients were diagnosed with first primary rectal cancer who had not received neoadjuvant therapy. These subjects were identified using the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database. The association between tumor size, lymph node status, distant metastases and cancer-specific mortality was investigated. Tumor size was examined as a continuous (1-30 mm) and categorical variable (11 size groups; 10-mm intervals). A non-linear correlation between increasing tumor size and the prevalence of lymph node involvement was observed, while a near-positive correlation between tumor size and distant metastases was presented. In addition, the 5-year and 10-year rates of rectal cancer-specific mortality were increased as the tumor enlarged. For small tumors (under 30 mm), a positive correlation was noted between tumor size and lymph node involvement. The clinical value of the tumor size should be reevaluated by exact classification.
Keywords: tumor size, lymph node status, distant metastases, rectal cancer, SEER

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact