3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(13):3769-3780. doi:10.7150/jca.51964 This issue Cite
Research Paper
OSCAR facilitates malignancy with enhanced metastasis correlating to inhibitory immune microenvironment in multiple cancer types
1. Department of Nutrition, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
2. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, People' hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750001, China.
3. Institute of Medical Research, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710072, China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Cancer Biology, National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases and Xijing Hospital of Digestive Diseases, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China.
5. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
* Equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
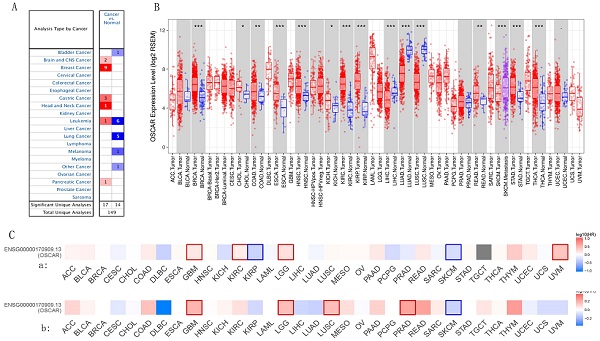
Cross talk between tumors and the immune microenvironment play a critical role in the malignant progression. The osteoclast-associated receptor (OSCAR) is a regulator of lymphocyte differentiation and maturation, but little is known about the role of OSCAR in multiple cancer types. We comprehensively analyzed OSCAR expression and explored its correlation with prognosis in multiple cancer types using Oncomine, TIMER, Gene GEPIA2 and CCLE. We examined OSCAR expression correlations with lymph node metastasis and pathological stage across tumor samples using UALCAN and GEPIA2. We analyzed the effects of OSCAR on survival using the Kaplan Meier plotter. We explored genes co-expressed with OSCAR using the LinkedOmics database and analyzed associated gene ontologies using Metascape. Further, we examined the correlation between OSCAR expression and immunocyte infiltration, markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and lymphocyte subtypes using TIMER. OSCAR mRNA levels were upregulated in most cancer types compared with adjacent normal tissues. Higher expression of OSCAR correlated with lymph node metastasis or advanced stage subgroups. High expression of OSCAR was related to low tumor purity, with increased levels of M2 macrophage polarization, T cells exhaustion, and mesenchymal phenotype in most cancer types. We also showed that the strength of OSCAR expression influence in malignant progression and inhibitory immune microenvironment is mitigated by the infiltration of natural killer cells. These findings shed light on the pro-carcinogenic role of OSCAR in most cancer types and indicate OSCAR could be targeted in future therapeutics to reverse the inhibitory immune microenvironment.
Keywords: OSCAR, immune microenvironment, macrophage, metastasis, prognosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact