3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(13):3967-3975. doi:10.7150/jca.45493 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Demethylzelasteral inhibits proliferation and EMT via repressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
1. School of clinical medicine, Affiliated Hospital, School of Public Health, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, Hebei 063000, China.
2. Department of Radiation Oncology, North China University of Science and Technology Affiliated People's Hospital, Tangshan, Hebei 063000, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
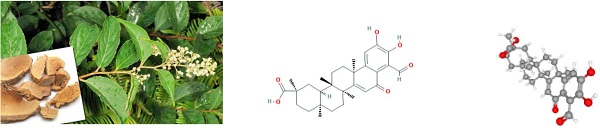
As a kind of tumor commonly seen, no effective treatment is available for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Therefore, seeking a new treatment is urgent. Demethylzeylasteral (T-96) isolated from Tripterygium wilfordii root bark embraces outstanding good antitumor activity. However, as for the mechanism of T-96 work on ESCC cells, it is rarely reported. In this study, we found that T-96 has inhibition when ESCC cells are proliferating, migrating and cloning. Moreover, relevant effects are influenced by dose and time. And T-96 can result in the stop of G2/M phase and induce apoptosis of ESCC cells. In addition, the expressions of Cyclin B1, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2, PARP1 and Survivin were decreased after starch demethylation. Despite of this, Bax and PARP1's expressions went up. To add up, there was an obvious increase in the expression of E-cadherin, while that of N-cadherin, Vimentin and MMP9 decreased after T-96 treatment. Moreover, the expression of Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, which concerns proteins β-Catenin, c-Myc and Wnt3a decreased. Our study shows that T-96 inhibits the proliferation and migration of esophageal cancer cells through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Moreover, it gives rise to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. According to the research results, T-96 tends to be put into use when treating ESCC patients, thus laying the experimental foundation for clinical research.
Keywords: Demethylzeylasteral, T-96, ESCC, proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, EMT, Wnt/β-catenin pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact