3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(15):4626-4637. doi:10.7150/jca.59740 This issue Cite
Research Paper
HOXA5 confers tamoxifen resistance via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ER-positive breast cancer
1. Department of Anatomy, Embryology Laboratory, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea.
2. Department of Anatomy, Graduate School of Medical Science, Bain Korea 21 Project, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea.
Abstract
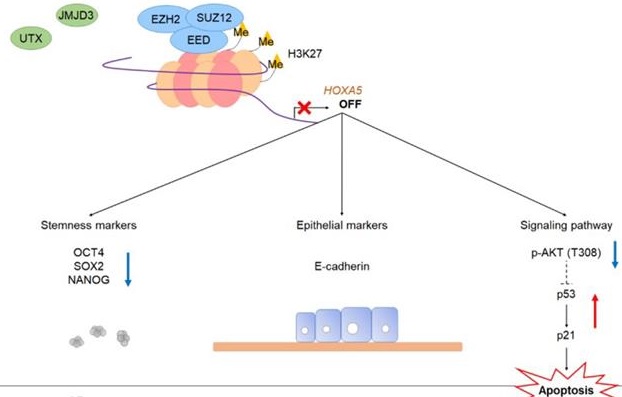
Tamoxifen is a commonly used drug to treat estrogen receptor-positive patients with breast cancer. Despite the outstanding efficacy of tamoxifen, approximately one-third of patients develop resistance toward it, thereby presenting a therapeutic challenge. HOX genes may be involved in the acquisition of tamoxifen resistance. In this study, we identified HOXA5, a member of the HOX gene family, as a marker of tamoxifen resistance. Using ChIP assay, we found that HOXA5 expression was significantly overexpressed in tamoxifen-resistant MCF7 (TAMR) breast cancer cells because of reduced H3K27me3 binding. HOXA5 upregulation resulted in activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling cascade, which in turn, led to p53 and p21 reduction, ultimately making the TAMR cells less apoptotic. Furthermore, elevated HOXA5 expression resulted in breast cancer cells acquiring more mesenchymal-like and stem cell traits associated with aggressive breast cancer phenotypes. In conclusion, our results delineate a mechanism by which HOXA5 promotes tumorigenesis, cancer progression, and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells.
Keywords: HOXA5, AKT, tamoxifen resistance, breast cancer, p53

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact