3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(16):4774-4779. doi:10.7150/jca.58168 This issue Cite
Research Paper
EIF5A expression and its role as a potential diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory Center, The Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, P.R. China.
2. Reproductive Medical Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
3. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
4. The First School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China.
5. Department of medicine, Kingsbrook Jewish Medical Center, 585 Schenectady ave, Brooklyn, New York, 11203, USA.
#These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
Introduction and objectives: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (EIF5A) is a member of the identified eIF family and played an important role in cell proliferation. There are few studies about the correlation between EIF5A and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
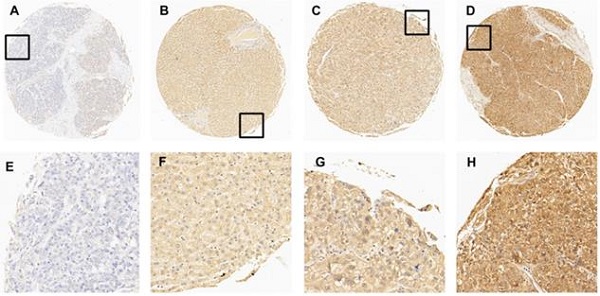
Materials and methods: We evaluated the expression of the EIF5A in human HCC cell lines and tissues by western blot analysis. Immunohistochemistry analysis of EIF5A was performed on a tissue microarray including 10 normal liver samples and 90 pathological section of HCC. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) was introduced to obtain an optimal cut-off score for EIF5A positive expression.
Results: Western blot results showed that EIF5A was highly expressed in HCC cell lines and tissues. Based on ROC curve analysis, 1/10 (10.0%) of normal hepatic tissues and 67/90 (74.4%) of HCC tissues were tested positive for EIF5A expression, which indicated that EIF5A were significantly up-regulated in HCC tissues compared with normal liver tissues (χ2=17.177, P<0.001). Furthermore, expression of EIF5A was significantly correlated with histological grade (P=0.048), clinical stage (P=0.003) and pT stage (P=0.003) but not correlated with sex (P=0.617) and age (P=0.831).
Conclusions: In our study, we demonstrated the expression of EIF5A is closely correlated with HCC. In consideration of its relationship with clinicopathological parameters including histological grade, clinical stage and pT stage of HCC, EIF5A could be a potential biomarker.
Keywords: EIF5A, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Tissue microarray, Diagnostic biomarker, Clinicopathological parameters

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact