3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(16):4945-4957. doi:10.7150/jca.53613 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PSMD7 downregulation suppresses lung cancer progression by regulating the p53 pathway
1. Department of Ultrasound, The Affiliated Zhangjiagang Hospital of Soochow University, 68 Jiyang West Road, Suzhou, 215600, China.
2. Department of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine, The Affiliated Zhangjiagang Hospital of Soochow University, 68 Jiyang West Road, Suzhou, 215600, China.
3. Department of Thoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Zhangjiagang Hospital of Soochow University, 68 Jiyang West Road, Suzhou, 215600, China.
4. Department of Emergency, The Affiliated Zhangjiagang Hospital of Soochow University, 68 Jiyang West Road, Suzhou, 215600, China.
5. Center for Translational Medicine, The Affiliated Zhangjiagang Hospital of Soochow University, 68 Jiyang West Road, Suzhou, 215600, China.
6. Department of General Surgery, The Affiliated Zhangjiagang Hospital of Soochow University, 68 Jiyang West Road, Suzhou, 215600, China.
Abstract
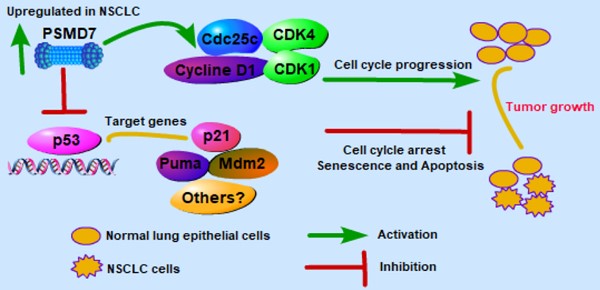
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women. The deubiquitinase PSMD7, as a core component of the 26S proteasome, is critical for the degradation of ubiquitinated proteins in the proteasome. Currently, PSMD7 expression and its roles in the progression of lung cancer remain largely unknown. In this study, we assessed PSMD7 expression and investigated the underlying molecular events by which PSMD7 regulates tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The results showed that PSMD7 is more highly expressed in NSCLC tissues than in adjacent noncancerous tissues. PSMD7 expression was also closely associated with lymph node invasion and the laterality of the tumor in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). A high PSMD7 level predicted poor overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in LUAD patients, and PSMD7 knockdown significantly reduced cell proliferation and induced G0/G1-phase cell cycle arrest, cell senescence and apoptosis. PSMD7 knockdown inhibited expression of a set of proteins regulating cell cycle progression. Depletion of PSMD7 increased p53 levels and induced p21 and puma expression in a p53-dependent manner. Importantly, knockdown of PSMD7 markedly inhibited LUAD tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. Taken together, these findings indicate that PSMD7 may serve as a valuable prognostic indicator and potential therapeutic target in LUAD.
Keywords: deubiquitinase, PSMD7, NSCLC, LUAD, p53, cell cycle proteins

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact