3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(19):5745-5752. doi:10.7150/jca.60596 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Co-overexpression of RIOK1 and AKT1 as a prognostic risk factor in glioma
1. Department of Human Anatomy, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province 110034, P.R. China.
2. Department of Pathology, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province 110034, P.R. China.
3. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Institute of Endocrinology, Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Endocrine Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, 110001, P.R. China.
4. Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Heping District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province, 110001, P.R. China
Abstract
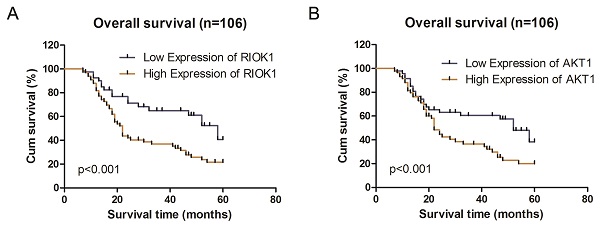
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most frequent primary malignancies of the brain. Although the treatment strategy has significantly improved, patient prognosis remains poor. In vitro studies have shown that the right open reading frame kinase 1/protein kinase B (RIOK1-AKT) signaling pathway plays an important role in the malignant phenotype of glioma cells. This study aimed to investigate the co-expression of RIOK1 and ATK in glioma tissues and its clinical significance. Compared with normal tissues, RIOK1 and AKT1 expression were significantly upregulated in glioma tissues. In addition, patients with higher World Health Organization staging grades had increased RIOK1 and AKT1 expression levels, and RIOK1 and AKT1 expression were positively correlated. Notably, both RIOK1 and AKT1 expressions were correlated with poor prognosis. In vitro experiments showed that silencing RIOK1 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cell lines by suppressing AKT and c-Myc expression. These results indicate that the RIOK1-AKT1 axis could play an important role in GBM progression.
Keywords: RIOK1, AKT1, c-Myc, GBM

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact