3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(19):5825-5837. doi:10.7150/jca.56640 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SNX-2112 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Downregulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
1. Medical Oncology Department, Affiliated Cancer Hospital & Institute of Guangzhou Medical University, No.78 Heng-Zhi-Gang Road, Yue Xiu District, Guangzhou 510095, China.
2. Oncology Center, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, No. 253 Industry Road, Guangzhou 510282, China.
3. Department of Oncology, Central South University Xiangya School of Medicine Affiliated Haikou Hospital, Hainan Province, 570208, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
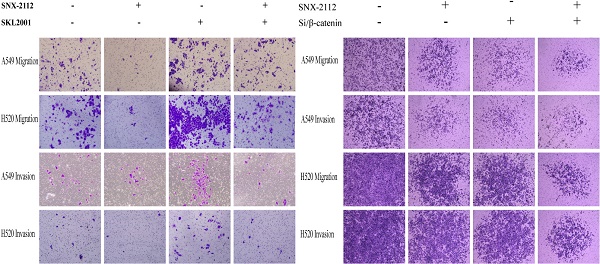
Lung cancer is the most frequent malignant tumor, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is responsible for substantial mortality worldwide. The small molecule SNX-2112 was recently shown to critically effect the proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells. Nevertheless, the precise mechanism by which SNX-2112 affects NSCLC remains poorly understood. Therefore, we investigated the function of SNX-2112 in NSCLC. We verified that SNX-2112 promoted apoptosis and suppressed the proliferation, invasion, and migration of A549 and H520 NSCLC cells in vitro. We further verified the potential mechanism of SNX-2112 in NSCLC. The changes in the protein levels demonstrated that SNX-2112 inhibited the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (increased E-cadherin and decreased N-cadherin and vimentin) and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (glycogen synthase kinase (GSK) 3β and phosphorylated (p)-β-catenin increased, β-catenin and p-GSK3β decreased) in NSCLC cells. These results were verified by rescue experiments using a Wnt/β-catenin pathway agonist. We also established a tumor xenograft model and confirmed that SNX-2112 reduced tumor growth and proliferation and enhanced necrosis and apoptosis in a NSCLC model in vivo. In conclusion, the current study is the first to discover the mechanism of SNX-2112 in NSCLC. SNX-2112 induced apoptosis and also inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration of NSCLC cells by downregulating EMT via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, SNX-2112, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, Wnt/β-catenin

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact