3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(19):5914-5922. doi:10.7150/jca.61581 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Suppression of human colon tumor by EERAC through regulating Notch/DLL4/Hes pathway inhibiting angiogenesis in vivo
Department of Coloproctology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, No 109 Xueyuan Western Road, Wenzhou, Zhejiang Province, 325000, P.R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this research.
Abstract
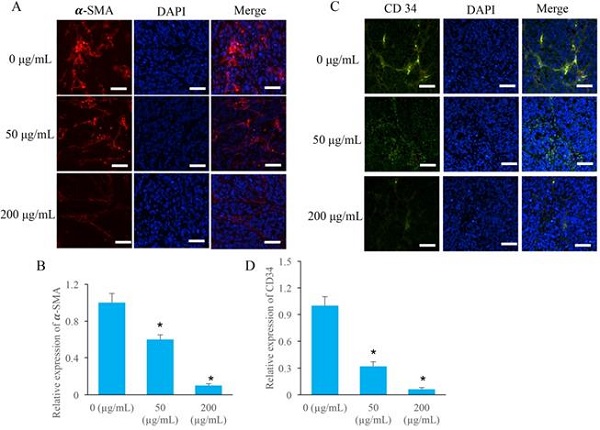
Background: Ethanol extracted from radix of Actinidia chinensis (EERAC) has been proved to be effective to inhibit colorectal cancer (CRC). Notch signaling pathway and angiogenesis in tumors are closely related with the progression of CRC. However, if EERAC could influence CRC through Notch signaling pathway and angiogenesis remains unclear.
Methods: Flow cytometry, transwell, wound healing methods were used to measure cell apoptosis, invasion, migration, and proliferation. Protein and mRNA expression were detected using qRT-PCR and western blotting. Immunofluorescence staining was applied to detect the expression of target protein in the tissues.
Results: The invasion, migration, and proliferation of CRC cells were remarkably suppressed by ERRAC. Significant promotion of cell apoptosis and cell ration in S stage were observed after EERAC treatment. The Notch1/DLL4/Hes1 signaling pathway and angiogenesis were suppressed by EERAC. Overexpression of LIM domain-binding 2 (LDB2) remarkably weakened the influence of ERRAC on the viability of CRC cells.
Conclusions: EERAC might suppress CRC through targeting Notch/DLL4/Hes1 pathway and inhibiting angiogenesis in tumors. This study might provide novel thought for the prevention and therapy of CRC through targeting Notch/DLL4/Hes1.
Keywords: CRC, Traditional Chinese medicine, Actinidia chinensis, Cancer, LDB2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact