3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(20):5991-5998. doi:10.7150/jca.61310 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Efficacy and Mechanism of Active Fractions in Fruit of Amomum villosum Lour. for Gastric Cancer
1. School of Traditional Dai-Thai Medicine, West Yunnan University of Applied Sciences; Jinghong, Yunnan 666100, China.
2. School of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University; Shanghai 200240, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
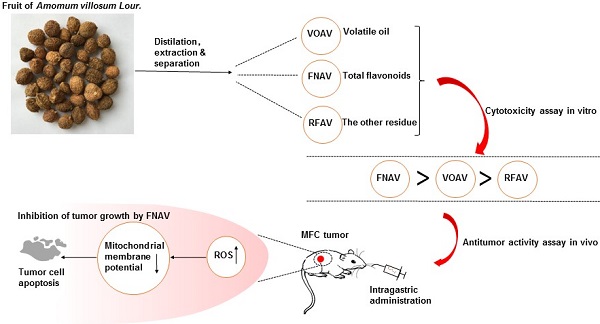
Amomi Fructus is the dried ripe fruit of Amomum villosum Lour. (A. villosum). It is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine widely used to treat gastrointestinal diseases, while the efficacy or mechanism of main components in Amomi Fructus on cancer treatment remains unknown. In this study, volatile oil of A. villosum (VOAV), total flavonoids of A. villosum (FNAV) and the other residue of A. villosum (RFAV) were distilled, extracted and separated as different active fractions of A. villosum. The cell toxicity test results indicated that VOAV and FNAV can effectively inhibit the cell growth of MFC cells. Flow cytometry test results confirmed that MFC cells were caused apoptosis after being treated with VOAV, FNAV or RFAV. VOAV, FNAV or RFAV induced MFC cells apoptosis through reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated mitochondrial pathway, evident by the increase of endogenous ROS and mitochondrial membrane potential collapse. In addition, FNAV exhibited robust inhibitory effects on MFC tumor growth, and could improve the health status of mice compared to that of mice in 5-FU treated group. To sum up, all the above results suggest that FNAV may be a good candidate for the development of new drugs for the treatment of gastric cancer.
Keywords: Amomum villosum Lour., gastric cancer, active fraction, efficacy, mechanism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact