3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(21):6484-6496. doi:10.7150/jca.62729 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Expression profile of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes as a prognostic biomarker for endometrial cancer
Department of Gynecology, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China.
#Co-first authors.
Abstract
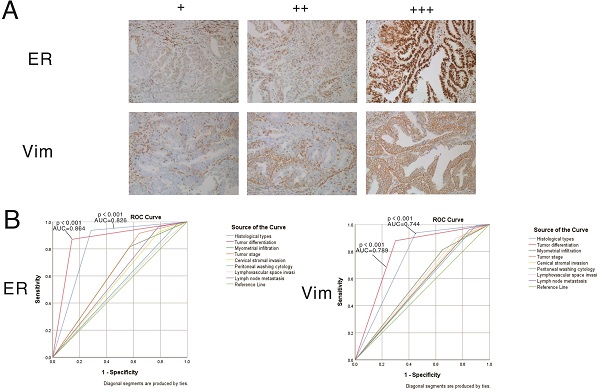
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is regulated by inducible factors, transcription factors, and a series of genes involved in diverse signaling pathways, which are correlated with tumor invasion and progression. In the present study, we analyzed the expression profile data of 1169 EMT-related genes in endometrial cancer (EC) from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset, and performed consistency clustering to divide EC samples into two subgroups based on overall survival. The genes differentially expressed between the two subtypes included EMT-related genes. Univariate Cox analysis and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) were applied to construct a prognostic model based on the 44 genes signature. Five genes (L1CAM, PRKCI, ESR1, CDKN2A, and VIM) were finally included to establish a formula for prognostic risk score. The low-risk group showed significantly better prognosis compared with the high-risk group in the TCGA dataset. In addition, the risk-scoring model successfully predicted prognosis in an external GEO dataset (GSE102073). The relationship between ERα and vimentin levels was confirmed through immunohistochemistry. In conclusion, these data indicate that the expression profile of EMT-related genes could predict prognosis in EC.
Keywords: endometrial cancer, EMT, prognosis, Cox analysis, The Cancer Genome Atlas, survival

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact