3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(22):6787-6795. doi:10.7150/jca.62352 This issue Cite
Review
The Role of miRNAs during Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Apoptosis in Digestive Cancer
1. Key Laboratory of Molecular Epidemiology of Hunan Province, School of Medicine, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, 410081, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Protein Chemistry and Developmental Biology of Fish of Ministry of Education, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, 410081, China.
3. Hunan Provincial Institute of Emergency Medicine, Hunan Provincial People's Hospital/The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University, Changsha, 410015, China.
4. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Hunan Provincial People's Hospital/The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University, Changsha, 410015, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
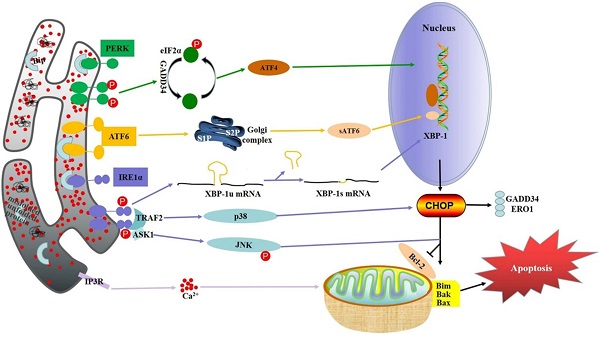
Digestive cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer mortality in the world. Despite a number of studies being conducted, the exact mechanism for treating digestive cancer has not yet been fully understood. To survive, digestive cancer cells are subjected to various internal and external adverse factors, such as hypoxia, nutritional deficiencies or drug toxicity, resulting in accumulation of misfolded and unfolded protein in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen further leading to ER stress and the unfolded protein response (UPR). During the last years, studies on the relationship between ER stress and microRNAs (miRNAs) has burst on the scene. miRNAs are non-coding RNAs with a length of 21~22nucleotides involved in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression, which could be regarded as oncomiRs (tumor inducers) and tumor suppressors regulating cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis by differently affecting the expression of genes related to cancer cell signaling. Therefore, investigating the interaction between ER stress and miRNAs is crucial for developing effective cancer treatment and prevention strategies. In this review, we mainly discuss miRNAs focusing on its regulation, role in ER stress induced apoptosis in Digestive cancer, expound the underlying mechanism, thus provides a theoretical foundation for finding new therapeutic targets of digestive cancer.
Keywords: ER stress, miRNAs, digestive cancers

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact