3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(23):6937-6947. doi:10.7150/jca.63235 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Mucin 1 promotes tumor progression through activating WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong 226001, P. R. China;
2. Department of Liver Surgery & Transplantation, Liver Cancer Institute, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Cancer Invasion, Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China;
3. Transfusion Department, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China;
4. Nanjing Foreign Language School, Nanjing 210018, P. R. China;
5. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China;
6. Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China
#These authors contributed equally to this work as first authors.
Abstract
Background: Current treatment options for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) are limited by the lack of understanding of the disease pathogenesis. It has been known that mucin 1 (MUC1) is a cell surface mucin that highly expressed in various cancer tissues. However, its role in ICC has not been well studied. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical significance and biological function of MUC1 in ICC.
Methods: qRT-PCR and western blot assays were performed to examine MUC1 expression. RNA-Seq (RNA Sequencing) s conducted to explore the RNA expression. A tissue microarray study including 214 ICC cases was also conducted to evaluate the clinical relevance and prognostic significance of MUC1. The role and underlying mechanisms of MUC1 in regulating cell growth and invasion were further explored both in vitro and in vivo models.
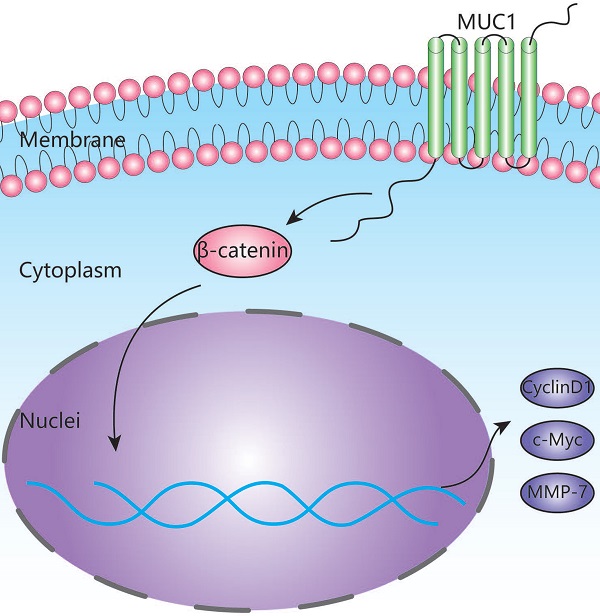
Results: The mRNA and protein levels of MUC1 were significantly up-regulated in ICC compared to paired non-tumor tissues. Depletion of MUC1 in HCCC9810 cells significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and overexpression of MUC1 in RBE cells resulted in increased cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Both univariate and multivariate analysis revealed that the protein expression of MUC1 was associated with overall survival and relapse-free survival after tumor resection. Clinically, high MUC1 expression was more commonly observed in aggressive tumors. Further studies indicated that MUC1 exerted its function through activating Wnt/ β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions: Our data suggests that MUC1 promoted ICC progression via activating Wnt / β-catenin pathway. This study not only deciphered the role of MUC in ICC pathogenesis, but also shed light upon identifying novel potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, mucin 1, Wnt/β-catenin pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact