3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(3):1048-1060. doi:10.7150/jca.66092 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LncRNA AC099850.3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion through PRR11/PI3K/AKT axis and is associated with patients prognosis
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Hubei Cancer Hospital, Wuhan 430079, China
2. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Hubei Cancer Hospital, Wuhan 430079, China
3. Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410000, Hunan, China
Abstract
Background: LncRNA is a key factor influencing tumor development. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of a novel lncRNA on the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: A candidate lncRNA in The Cancer Genome Atlas database was identified using limma and survival R packages. The effect of lncRNA AC099850.3 on cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion, as well as its association with immune cells in HCC were investigated. Furthermore, the functional mechanisms of lncRNA AC099850.3 in HCC were elucidated.
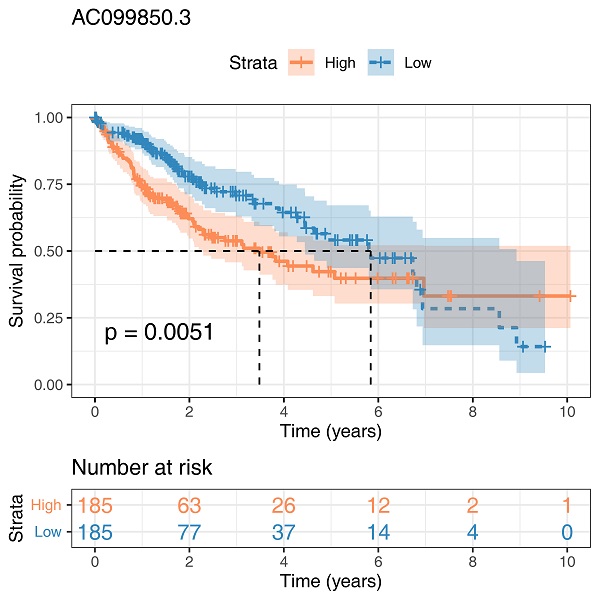
Results: The aberrant expression of lncRNA AC099850.3 was identified in tumor tissues and its prognostic relevance in HCC was determined. The results revealed that AC099850.3 was highly expressed in HCC tissues and cell lines, and it predicted poor prognosis in patients with HCC. Furthermore, knockdown of AC099850.3 significantly suppressed the proliferation and metastatic potential of HCC cells, and promoted cell apoptosis in HCC cells. The results of gene set enrichment analysis revealed that the PI3K/AKT pathway was associated with the biological function of AC099850.3, which was further validated by western blotting. PRR11 was identified as the target gene of AC099850.3 and we established that AC099850.3 acted as an oncogene in the PRR11/PI3K/AKT axis. Immune cell infiltration analyses results revealed that AC099850.3 was positively correlated with T follicular helper cells, M0 macrophages, CD4+ memory T cells, and memory B cells. Conversely, AC099850.3 was negatively correlated with M2 macrophages, monocytes, natural killer cells, and CD8+ T cells, which could be responsible for its oncogenic effect. Of note, a significantly positive correlation was observed between AC099850.3 and key immune checkpoint molecules (PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, and CTLA4) in the present study, making AC099850.3 a potential immune therapeutic target for HCC.
Conclusion: AC099850.3 can promote malignant biological behavior of HCC cells, and could be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: LncRNA, AC099850.3, hepatocellular carcinoma, PRR11, PI3K/AKT, tumor immunity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact