3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(3):1061-1072. doi:10.7150/jca.64195 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 mediated glutaminolysis sustains HCC cells survival under glucose deprivation
1. The Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology of Infectious Diseases designated by the Chinese Ministry of Education, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, 400016, China
2. Department of Medical examination center, The second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
3. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Army Medical University, Chongqing, 400037, China
4. Department of Endocrine and Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
* These authors contribute to the equal work.
Abstract
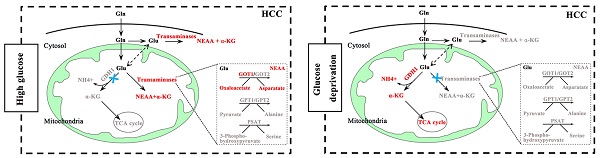
Besides aerobic glycolysis, glutaminolysis has also become a hot spot in the field of tumor research because of its important role in regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration and invasion. Meanwhile, it is generally believed that tumor cells could sustain its proliferation and survival according to a so-called metabolic flexibility. How the metabolic flexibility of HCC cells behaves has not yet been fully elucidated. In this study, we validated the glutamine addiction of HCC cells, and identified that the glutaminolysis pathway of HCC cells altered in response to different glucose conditions. That is, glutamate transaminases GOT1 pathway played a dominant role in regulating cell growth when glucose was sufficient, yet deaminase GDH1 mediated metabolic pathway became dominant when glucose was limited, for the reason that GDH1 could drive the TCA cycle in response to glucose deprivation. Additionally, we further uncovered an negative relationship between GDH1 and GOT1 in low-glucose HCC tissues. Together, our study provided a new insight into the metabolic flexibility of glutaminolysis related enzymes in HCC, and highlighted the crucial role of GDH1 on HCC cells proliferation and survival in glucose starvation.
Keywords: HCC, Glutaminolysis, GDH1, TCA cycle

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact