3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(5):1679-1684. doi:10.7150/jca.69136 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Application of Prostate Resection Endoscopy for Treating Acute Obstruction Associated with Rectal Cancer
1. Department of General Surgery II, Hexi University Affiliated Zhangye People's Hospital, Zhangye Gansu, 734000, China
2. Department of Endoscopy Center, Hexi University Affiliated Zhangye People's Hospital, Zhangye Gansu, 734000, China
3. Department of Urology, Hexi University affiliated Zhangye People's Hospital, Gansu 734000, China
4. Institute of Urology, Hexi University, Zhangye Gansu, 734000, China
*Peng Yan, Yujie Qin contributed equally to the work.
Abstract
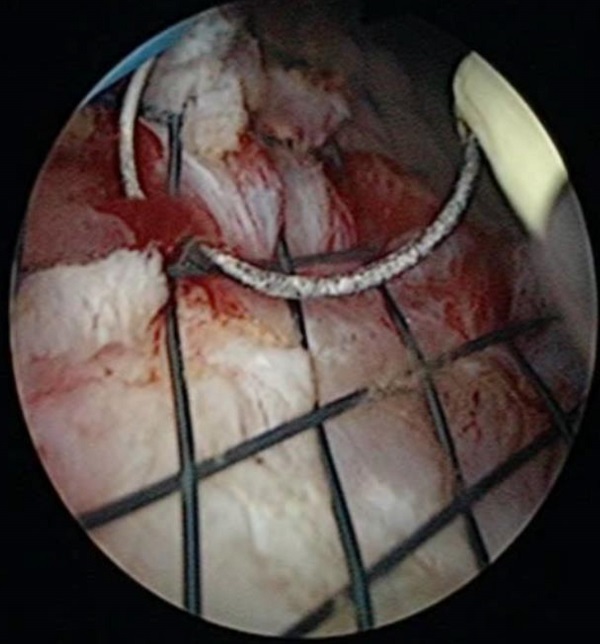
Purpose: To explore a minimally invasive emergency solution for acute obstruction caused by rectal cancer in patients in whom rectal stents or drainage tubes cannot be placed under the guidance of conventional colonoscopy or digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Patients and Methods: Without anesthesia, analgesia, or sedation, the prostate resection endoscopy was inserted into the rectum through the anus, and the rectal space in which the tumor caused obstruction was searched with a certain flushing pressure until it crossed the area of obstruction to reach the proximal intestinal cavity. The drainage catheter or rectal stent was inserted through the sheath of the endoscope to relieve the acute obstruction and permit further cancer treatment.
Results: In 31 patients in whom a drainage catheter or rectal stent could not be inserted using conventional colonoscopy or DSA guidance, placement of the catheter or stent into the proximal intestinal cavity was achieved in 28 patients, including drainage tube placement in 21 patients and rectal stent placement in seven patients. Three patients could not undergo placement because of their advanced age and poor general condition. The operative time ranged 15-40 min. Among the 28 patients whose obstruction was relieved, 23 patients underwent radical resection rectal cancer after 10-14 days, and five patients were discharged with stents because they were unwilling to receive further treatment. There were no postoperative complications.
Conclusion: Transanal resection is a minimally invasive, effective, safe, and feasible emergency treatment for rectal cancer-associated obstruction.
Keywords: resectoscope, rectal cancer, obstruction

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact