3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(6):1871-1881. doi:10.7150/jca.62454 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Investigating the Association between COMMD3 Expression and the Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200071, China.
2. First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui 230022, China.
3. Nanjing Hospital of Chinese Medicine affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210001, China.
4. Luan Hospital of Chinese Medicine affiliated to Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Luan 237001, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
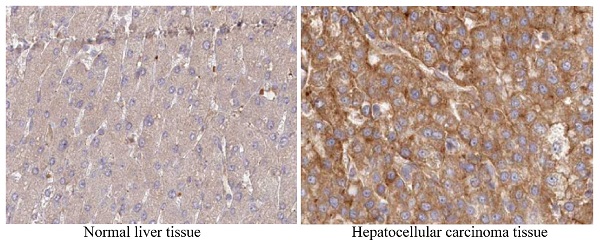
The Copper Metabolism MURR1 Domain (COMMD) family proteins are known to play roles in promoting or inhibiting the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells. However, the role of COMMD3 in hepatocellular carcinoma are still unclear. By investigating the TCGA datasets, we found that the mRNA expression of COMMD3 was significantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue compared with normal liver tissue, which was further supported by Oncomine dataset, Western blot, qRT-PCR, and IHC analysis. Moreover, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the high expression of COMMD3 was associated with poor overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). Consistently, the clinic-pathological analysis found that the overexpression of COMMD3 was correlated with advanced TNM stage, advanced T stage and vascular invasion. By performing multivariate analysis, we found that the expression of COMMD3 was an independent influencing factor on OS and DFS. Furthermore, we knocked down COMMD3 in HCC cells via RNA interference. The results showed that silencing COMMD3 could inhibit the migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of HCC cells. Finally, we established xenograft tumor model in nude mice, and the knockdown of COMMD3 suppressed tumor growth and angiogenesis. In summary, our study showed that the high expression of COMMD3 was correlated with poor prognosis in HCC patients and contributed to migration, invasion and angiogenesis of HCC cells.
Keywords: COMMD3, mRNA, prognosis, hepatocellular carcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact