3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(6):1985-2000. doi:10.7150/jca.69544 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ASF1b is a novel prognostic predictor associated with cell cycle signaling pathway in gastric cancer
1. Department of Surgical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, China.
2. Department of Organ Transplantation, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Navy Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200003, China.
Abstract
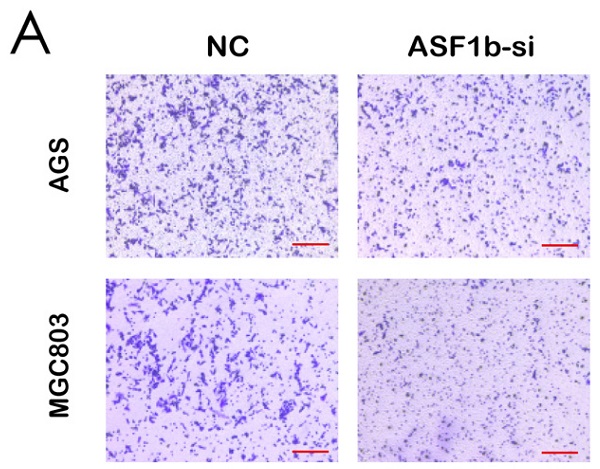
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common malignant tumors with poor outcomes. Identification of new therapeutic targets is urgently needed. Accumulating evidence has shown that anti-silencing function 1b (ASF1b) contributes to the progression in multiple cancer types. However, detailed mechanisms of ASF1b tumorigenesis in gastric cancer remain elusive. This study showed that ASF1b was upregulated in GC tissues and remarkably correlated with TNM stage, histological grade and poor prognosis of GC. We induced down and up-regulation of ASF1b in GC cell lines and monitored the changes in their biological behavior. Furthermore, loss of ASF1b was efficient to suppress subcutaneous xenograft tumor growth in vivo. We demonstrate that ASF1b is involved in regulation of cell cycle and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling through experiments and database analysis. Mechanistically, ASF1b promoted the proliferation, migration and invasion of GC cells. Taken together, this study highlights the role of ASF1b, which provided new insights into the underlying mechanism of progression and metastasis in GC for the first time.
Keywords: Gastric cancer, ASF1b, cell cycle, cell proliferation, prognosis, PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact