3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(7):2362-2373. doi:10.7150/jca.71263 This issue Cite
Review
Low Intensity Ultrasound as an Antidote to Taxane/Paclitaxel-induced Cytotoxicity
1. Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL 33136
2. Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Science, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL 33136
3. Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, 1120 NW 14th Street, Miami, FL, USA
Received 2022-1-20; Accepted 2022-4-4; Published 2022-4-18
Abstract
The taxane family of compounds, including Taxol/paclitaxel and Taxotere/docetaxel, are surprisingly successful drugs used in combination or alone for the treatment of most major solid tumors, especially metastatic cancer. The drugs are commonly used in regimen with other agents (often platinum drugs) as frontline treatment, or used as a single agent in a dose dense regimen for recurrent cancer. The major side effects of taxanes are peripheral neuropathy, alopecia, and neutropenia, which are grave burden for patients and limit the full potential of the taxane drugs. Especially in the current treatment protocol for peripheral neuropathy, taxane dosage is reduced once the symptoms present, resulting in the loss of full or optimal cancer killing activity.
Substantial efforts have been made to address the problem of cytotoxic side effects of taxanes, though strategies remain very limited. Following administration of the taxane compound by infusion, taxane binds to cellular microtubules and is sequestered within the cells for several days. Taxane stabilizes and interferes with microtubule function, leading to ultimate death of cancer cells, but also damages hair follicles, peripheral neurons, and hemopoietic stem cells. Currently, cryo-treatment is practiced to limit exposure and side effects of the drug during infusion, though the effectiveness is uncertain or limited.
A recent laboratory finding may provide a new strategy to counter taxane cytotoxicity, that a brief exposure to low density ultrasound waves was sufficient to eliminate paclitaxel cytotoxicity cells in culture by transiently breaking microtubule filaments, which were then relocated to lysosomes for disposal. Thus, ultrasonic force to break rigid microtubules is an effective solution to counter taxane cytotoxicity. The discovery and concept of low intensity ultrasound as an antidote may have the potential to provide a practical strategy to counter paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy and alopecia that resulted from chemotherapy.
Taxanes are a class of important drugs used in chemotherapy to treat several major cancers. This article reviews a new laboratory discovery that ultrasound can be used as an antidote for the peripheral cytotoxicity of taxane drugs and discusses the potential development and application of low intensity ultrasound to prevent side effects in chemotherapeutic treatment of cancer patients.
Keywords: Ultrasound, shock wave, microtubules, Taxol/paclitaxel, cytotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, alopecia, neutropenia, cancer chemotherapy, side effects
1. Cancer chemotherapy: taxanes/paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (brand name Taxol) is a key drug in the current treatment of several major solid tumors, including ovarian cancer [1,2]. A paclitaxel dose-dense protocol is also effective to treat recurrent ovarian cancer [3-5]. Paclitaxel targets tubulin, and alters the dynamics and stabilizes microtubule filaments [6-8], leading to cell death [9-11]. The major side effects (neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, and alopecia) are thought to be caused by the impact of paclitaxel on the dynamics of the microtubules and killing of mitotic cells [12], including rapidly dividing matrix keratinocytes in the hair follicles [13,14] and the replenishment of neutrophils [15]. The interference of paclitaxel on neuronal microtubule dynamic remodeling leads to peripheral neuropathy.
Although generally paclitaxel is highly effective with tolerable side effects, several key side effects include peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia, and alopecia [15]. Neutropenia and alopecia are putatively caused by the high proliferative activity of the hematopoietic stem cells and matrix cells of the hair follicles, respectively. The presentation of peripheral neuropathy is assumed because of the critical roles of microtubules in the function and maintenance of neuronal axons.
2. Taxane/paclitaxel mechanism of action
Paclitaxel, the first Taxane class of compounds, is a surprisingly successful anti-cancer drug [2,5,16]. Paclitaxel was first identified to have cytotoxicity to cancer cells in a search for anti-cancer activity from compounds derived from plants, in paclitaxel's case the Pacific yew tree (Taxus brevifolia) [10,12,17]. The discovery of its activity to bind and stabilize microtubules [6-8] and consequently inhibit mitosis [9-11] prompted its clinical development.
The traditional view, largely based on studies of paclitaxel on cancer cells in culture, is that paclitaxel binds and stabilizes microtubules, and the key consequences relevant to its efficacy is mitotic inhibition and ultimately apoptosis [8,9,18]. Additional studies indicate that slippage in mitotic inhibition and the aberrant mitosis and mitotic catastrophe that result are an important mechanism in the efficacy of paclitaxel treatment [10,19].
However, alternative opinions of a minority contend that paclitaxel also kills cancer cells by a non-mitotic mechanism [20-24], which may be even more important than targeting the proliferative characteristic of cancer cells. Remarkably, paclitaxel killing is p53-independent as high grade ovarian cancer generally has inactivated p53 [16], and the cancer cells are commonly insensitive to apoptotic stimulation [19]. Several studies also suggest that paclitaxel appears not to directly stimulate the activation of caspase-3, and its efficacy is independent of caspase-3 activation or through a classical apoptosis pathway [19].
Nevertheless, the observations are consistent that microtubules are the specific and relevant drug targets [16]. Another observation is that paclitaxel causes the formation of multiple micronuclei without chromatin condensation in cancer cells, a phenomenon coined as “micronucleation”, to distinguish from “nuclear fragmentation” that describes apoptosis and involves chromatin condensation [19]. This formation of multiple micronuclei is proposed to be important for cancer killing through the activation of the innate immunity and inflammatory pathway [19].
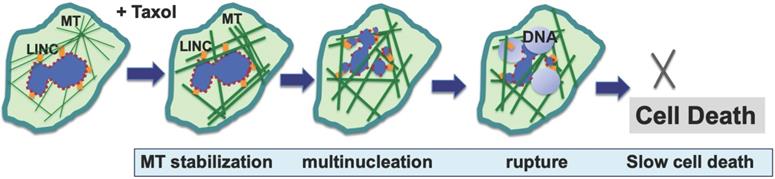
Generally, in the presence of paclitaxel and its interference on microtubule function, the formation of multiple micronuclei likely results from aberrant, multipolar mitosis [10,19]. A new study proposes a non-mitotic mechanism for the paclitaxel-stimulated formation of micronuclei, as the rigid microtubule bundles associating with the nuclear envelope physically pull and distort the structure [25]. The proposal of a physical force exerted by paclitaxel-induced rigid microtubule filaments in breaking malleable cancer nuclei provides a non-mitotic mechanism to generate multiple micronuclei [24,25] (Fig. 1). This proposed mechanism offers a possible alternative explanation for the well-established dogma that paclitaxel targets mitosis in cancer therapy; rather, paclitaxel likely aims at the weakened nuclear envelope of malignant cells. The study provides a new realization that paclitaxel can induce the generation of micronuclei in cells at S-phase by a non-mitotic mechanism [25]. In addition, for paclitaxel to target proliferative, mitotic cells, the nuclear envelope malleability appears to be another characteristic that favors cancer versus benign cells. The loss or reduction of nuclear lamina proteins, especially Lamin A/C, in cancer cells has been previously noted [26-29]. Thus, malleability of cancer nuclear envelope provides another specificity for paclitaxel, in addition to cell proliferation [24].
Another observation is that a brief treatment of ovarian cancer cells with paclitaxel induced the formation of rare cells with enlarged and deformed nuclei, likely a result of suppression of mitosis but continuous genomic replication [30]. These cells, termed “polyploid giant cancer cells” (PGCCs) have been found also to be present in cancer tissues and to harbor characteristics of stem cells found in early embryos [31]. An emerging concept, established by a series of publications in the last decade [30-33], proposes that the PGCCs are ovarian cancer stem cells, and they may account for the ability of cancer to gain resistance to chemotherapy [32,33]. In a previous study giving similar idea, the paclitaxel-induced multinucleated cells were suggested to associate with paclitaxel resistance [34]. Thus, paclitaxel-induced nuclear structural changes have interesting implications in ovarian cancer progenitor cells, mechanisms in paclitaxel cell killing, and drug resistance.
3. Retention of paclitaxel within affected cells
The pharmacokinetic properties of paclitaxel in human patients have been documented [35]. Paclitaxel is commonly administrated by infusion over several hours. Although a high plasma concentration is reached, the level in blood declines rapidly following infusion, with a half time of just hours [35]. Very little paclitaxel or its metabolites are secreted through urine, and sequestration of paclitaxel in tissues/cells is likely a key mechanism in the clearance of the drug [36].
Tumor cells and normal tissues take up and sequester abundant drugs into cells during the infusion, at several hundreds of times the concentration found in the extracellular space [8,18]. Paclitaxel binds with high affinity to alpha-tubulin within microtubules at nearly a 1:1 stoichiometry [37], and the concentration of tubulin in cells is calculated to be in the range of 10-20 µM [8,18,38,39]. The ability of cells to uptake and concentrate paclitaxel results in part from paclitaxel sequestration by binding to abundant microtubules and tubulins [8,18,38,39]. Intracellular paclitaxel is not washed out, but rather retained over several days after exposure, during which time the rigid microtubules persist [8,18,40,41].
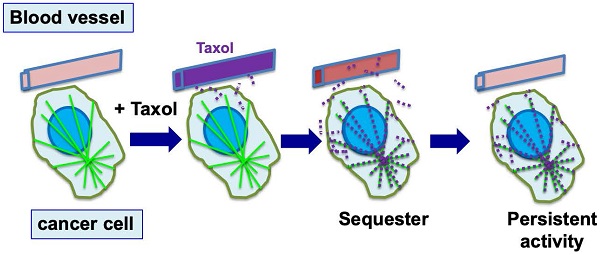
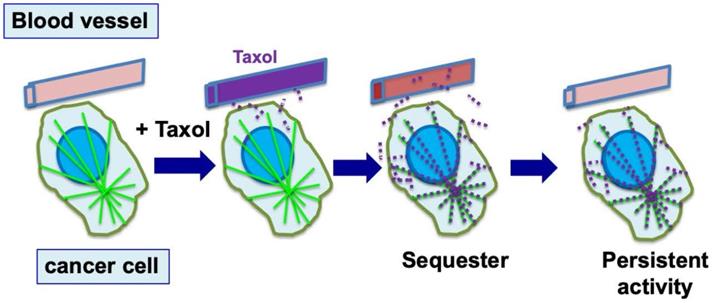
In laboratory studies, paclitaxel was found to be concentrated several hundred-fold into cultured cells [8,37]. In animal and patient studies, paclitaxel was found present from several days to a week within cells and tumor tissues, though the drug level had been well cleared in plasma [41,42]. Thus, following drug administration, paclitaxel is sequestered and retained within cells by binding to microtubules for a prolonged period of time. Paclitaxel activity persists, resulting in the death of the cancer cells over a few days. However, the persisting activity also causes undesirable side effects (Fig. 2). Although it seems to have not been emphasized, this unique property of intracellular paclitaxel retention is likely an important factor for the success of paclitaxel as an anti-cancer drug.
Microtubules are polymers of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers, and play multiple roles in cellular functions [43,44]. Microtubules are dynamic: the filaments are constantly extending and shortening, with a balance between the cellular pool of alpha- and beta-tubulin dimers and microtubule polymers, which are about half and half under normal conditions [39,45]. Paclitaxel promotes 90-100% of tubulins into polymerized forms [39,45,46].
Proposed mechanisms for paclitaxel-induced breaking of the nuclear envelope and multiple micronucleation in cancer killing. Based on new studies, a mechanism has been suggested for the anti-cancer activity of paclitaxel: paclitaxel induces disorganized and rigid microtubule (MT) bundles, which apply physical forces to the nuclear envelope through LINC (linker of nuclear and cytoskeleton) bridges, resulting in the breaking of associated malleable nuclei of neoplastic cells and the formation of multiple micronuclei. Paclitaxel induces breaking of nuclear envelope in both mitotic and non-mitotic cancer cells. The micronuclei are defective in membrane structure (illustrated by dotted outline) and have high propensity for rupture and release of chromatin material, resulting in compromised nuclear structure and cell death.
Cellular sequestration and retention of paclitaxel enables efficient killing of tumor cells. During chemotherapy, paclitaxel (Taxol) is administrated to patients over 3-6 hours, and reaches a peak concentration in plasma by the end of drug infusion. Over the next 6 to 10 hours, paclitaxel level declines rapidly, and the drug is concentrated in cells (largely by binding to microtubules) several hundred times over the blood level (illustrated by red dots). By binding to microtubules, paclitaxel persists at high levels inside cells for the next 3 to 7 days, where the drug triggers nuclear envelope breakage and the death of cancer cells.
Tubulins are relatively stable, and the tubulin protein is removed by proteasome- (but not lysosome-) mediated degradation [47] and via degradation by cathepsin D [48]. Because of the importance of microtubules in cellular function, the homeostasis of tubulins is tightly regulated [49,50]. Tubulins control their synthesis by autoregulation at the mRNA stability [51]. Thus, addition of paclitaxel to eliminate alpha- and beta-tubulin dimers (into polymers) stimulates production of new tubulins. Newly synthesized tubulins will further sequester paclitaxel until all available drugs are depleted.
4. Taxane side effects: pathology and mechanisms
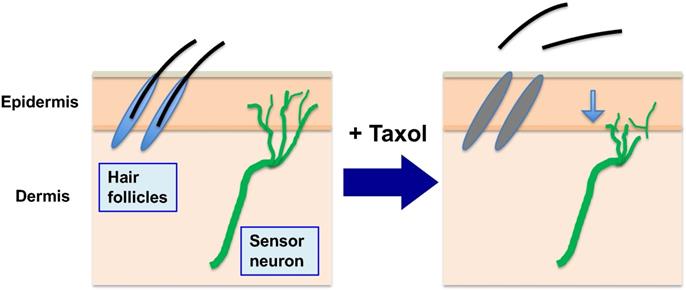
The common side effects of taxane chemotherapy are neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, and alopecia [15] (Fig. 3). Both neutropenia and peripheral neuropathy are often the dose limiting factors in cancer treatment using taxanes [15], and effective interventional procedures would be highly valuable, but are not available currently. Alopecia, though it may not limit treatment protocol, is nevertheless a distressful quality-of-life issue for many cancer patients and is the top concern voiced by patients during consultations of chemotherapy treatment [52]. These side effects are explained by the targeting of microtubules in the host cells, either with roles in mitosis for hematopoietic stem cells or for matrix cells in hair follicles, resulting in neutropenia or alopecia, respectively, or a role in axonal maintenance and function resulting in peripheral neuropathy.
Neutropenia is the principal dose-limiting toxicity of paclitaxel with an early onset (around day 8), when neutrophil counts drop by day 8 to day 11, followed by rapid recovery on days 15 to 21 [15]. Neutropenia is not cumulative, suggesting that the drug does not permanently damage the hematopoietic stem cells, which seem to be able to recover fully. Obviously, for hematopoietic stem cells, which are one of the most proliferative cell types, inhibition of mitosis by paclitaxel impedes renewal of the immune cells [15]. However, the suppression of white blood cells often is transient, and the neutrophil level often can recover in a few days [15]. Additionally, the issue when presented is routinely managed by giving granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) to enhance the expansion of hematopoietic stem cells [15].
Another highly proliferative cell type is the matrix cells of the hair follicles. Hair follicles undergo cycles of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), and relative quiescence (telogen) throughout life [53]. In humans, normally 85~90% of scalp hair follicles are in anagen at any given time, when hair follicle matrix cells undergo rapid proliferation, making them extremely susceptible to mitotic inhibitors such as paclitaxel. Paclitaxel induces massive mitotic defects and apoptosis in transit amplifying hair matrix keratinocytes and also severely damages epithelial stem/progenitor cells in the bulge and outer root sheath of human scalp hair follicles [14]. This results in hair shedding that begins as early as 1-3 weeks after initiation of chemotherapy [13,54]. More than 80% of patients receiving paclitaxel develop alopecia, and beard, eyebrows, and eyelashes can also be affected, in addition to scalp hair. Hair regrowth usually takes 3~6 months after cessation of chemotherapy, but in a substantial number of cases, hair loss is irreversible [52,55]. While killing of mitotic hair matrix keratinocytes accounts for the drastic hair loss, direct epithelial stem cell damage likely causes irreversible hair loss [14].
Sensory neuropathy, presenting as numbness and pain of feet and hands, is often the dose-limiting toxicity of the taxane agents [12,15,56,57]. In this case, mitosis is not the target in this terminally differentiated cell type. However, microtubules play critical functions in neuronal axons, and paclitaxel targeting would cause a pathological situation. This major side effect (peripheral neuropathy) is thought to be caused by the impact of paclitaxel on the dynamics of the axonal microtubule structure, presumably altering the distribution and structure of the peripheral neuron network and the transmission of nerve stimuli [12,58]. Clinical features of peripheral neuropathy often present with a reduced density of peripheral neuron fibers, visualized using diagnostic ultrasound [56,59,60](Fig. 3). Extensive laboratory research using cell systems, nonmammalian animal models, and rodent models has been attempted and is ongoing to understand the complex mechanisms of paclitaxel in causing peripheral neuronal damage [61-63]. Paclitaxel causes neurite retraction in these cultured neuronal cells, and it is considered that the phenomenon models the neuronal damage in paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy [12]. Although the binding and stabilization of neuronal microtubule bundles by paclitaxel is thought to be the initial cause, the subsequent pathways and mechanisms leading to neuronal damage are complex and remain unresolved.
5. Research efforts to counter paclitaxel/taxane side effects
Oncologists have invested substantial research effort to find strategies to counter the side effects and fully realize the power of taxanes in the treatment of a wide range of cancer types [15]. Developing a practical strategy to prevent the side effects of paclitaxel is indeed a difficult problem to solve, and various models have been used to investigate [63]. Potential drugs to block paclitaxel cytotoxicity will also inhibit the cancer killing activity, making the potential drugs unusable. Many studies tested agents with alternative mechanisms, though so far none have been found to reduce the symptoms [63,64].
The underlying pathobiology of paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced alopecia remains poorly understood. Recently it was shown that paclitaxel induces massive mitotic defects and apoptosis in transit amplifying hair matrix keratinocytes and also severely damages epithelial stem/progenitor cells in the bulge and outer root sheath of human scalp hair follicles [14]. This newly identified damage directly to stem/progenitor cells likely explains the severity and permanence of paclitaxel-induced alopecia. Since paclitaxel, as a mitotic inhibitor, targets cells at mitosis, or the M phase of the cell cycle [10,11,65], blocking of hair matrix cells from entering into mitosis is a potential strategy to prevent hair follicle damage and possibly alopecia. Indeed, using the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib to keep cells of human hair follicles in organoid culture in G1, paclitaxel-induced apoptosis (shown by caspase-3 activation) is prevented [14]. This concept has been applied to test CDK4/6 inhibition for the protection against chemotherapy-induced acute kidney injury [66,67] and chemotherapy-induced hematopoietic stem cell exhaustion [68]. However, systematic blocking of mitosis likely will also reduce efficacy of paclitaxel activity in chemotherapy. Additionally, the CDK4/6 inhibitor itself already presents alopecia as a side effect [69-71]. Thus, the possibility of using the CDK4/6 inhibitor to prevent paclitaxel-induced alopecia may require fine calibration of drug dosage and drug administration sequence and schedule.
In addition to neutropenia, which is often transient and readily recoverable, severe peripheral neuropathy is accumulative and is often the dosage limiting factor in treatment using taxane drugs [15,36]. In patient biopsies and animal models, paclitaxel treatment was observed to induce reduction of sensory neuron ends [63]. In vitro studies indicate that paclitaxel causes neurite retraction and neuron cell degeneration, leading to the idea that paclitaxel targeting of axon microtubules is the cause of neuronal retraction and peripheral neuropathy [58,72]. However, some studies indicate peripheral neuropathy may precede axon retraction [73,74]. Although the initial step appears to be the paclitaxel binding to axonal microtubules and their stabilization, downstream pathways leading to the pathology are more complex [63].
Many studies and various proposed mechanisms have been reported [63]. As an example, studies propose that the damage to epidermal mitochondria and generation of H2O2, and subsequent activation of MMP-13, are involved in neurite degeneration [62,75]. Upregulation of MMP-13 by paclitaxel has also been confirmed in mammals to be a potential mechanism for paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy [62,75]. MMP-13 is a member of the matrix-metalloproteinase family of matrix-degrading enzymes, and its suppression likely will not affect the activity of paclitaxel in killing cancer cells. Thus, pharmacologic inhibition of MMP-13 may be a potential strategy to prevent paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy [62,75].
Alopecia and peripheral neuropathy (in addition to neutropenia) are the main side effects of paclitaxel in chemotherapy. During chemotherapy to kill cancer cells, paclitaxel (Taxol) is administrated to patients over several hours (3 to 6 hours), and the drug is sequestered and concentrated in both tumor and normal cells (by binding to microtubules). While paclitaxel presented in high levels inside cells triggers death of cancer cells over the next 2-3 days, it also causes death of the proliferative hair matrix keratinocytes, leading to shedding of the hair shaft and alopecia. The retained paclitaxel also damages and causes retraction of sensory neuron terminals, causing peripheral neuropathy. (Noted that neutropenia is another major side effect, not illustrated here).
Despite their recognized importance and the extensive efforts devoted to the issues related to paclitaxel side effects, to date, few approaches are practical and available to counter taxane side effects in chemotherapy [63]. The mechanisms of paclitaxel induced neuronal damage and development of peripheral neuropathy have been extensively explored, and many drugs and agents have been suggested to have neuroprotective effects in basic laboratory studies. Some of these drugs have been tested in clinical studies for their protective effects. In the pre-clinical research, these neuropathy inhibitors are proposed to have mechanisms targeting oxidative stress, inflammatory response, ion channels, transient receptor potential channels, cannabinoid receptors, and the monoamine nervous system. However, very few drugs have demonstrated any efficacy in protecting paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in clinical trials [64], and none has reached clinical utility.
6. Prevention of taxane chemotherapy side effects using cryo-treatment
Currently, no satisfactory methods are available to reverse the side effects of paclitaxel, though cooling of hands and feet to limit drug exposure has been studied as a possible strategy to limit peripheral neuropathy of hands and feet [76,77]. For protection from hair loss, only scalp cooling has been established as a method to limit drug exposure to the scalp and to prevent or reduce alopecia [78], but its success is limited and unpredictable [79,80], and scalp cooling caps cannot protect eyebrows, eyelashes and facial hair. Therefore, novel approaches to prevent paclitaxel-induced alopecia are urgently needed to improve the quality of life of cancer patients.
The cooling needs to be maintained during the entire paclitaxel infusion period, generally 3 to 6 hours [35]. Cooling hands and feet with cooling gloves and socks, or the scalp with a cold hat/cap, works to limit the blood flow and thus the exposure to drugs. However, possible mechanisms such as the impact of temperature on microtubules polymerization, and slowing the rate and number of mitotic hair follicle matrix keratinocytes that enter mitosis, may also contribute to the outcome.
7. Discovery that low intensity ultrasound to be an antidote for paclitaxel cytotoxicity
The new discovery that low intensity ultrasound is an antidote of paclitaxel cytotoxicity [81] may offer a unique and effective strategy to eliminate the side effects of paclitaxel in cancer chemotherapy.
Ultrasound technologies have extensive applications in medicine, either for diagnosis (sonogram) or therapy [82-84]. Typically, ultrasound with extremely low intensity (1-50 mW/cm2) and high frequency (such as 50 MHz) is used for diagnostic (imaging) purposes. High intensity (> 8 W/cm2, 20-60 kHz) ultrasound that can deliver strong energy is used for surgery and disruption through heating and acoustic cavitation. The medical application of ultrasound with an intensity that is low yet sufficiently high to produce biological activity is known as ultrasound physiotherapy [83,84], which uses sufficiently strong but non-disruptive ultrasound shock waves (0.5-3.0 W/cm2). The most commonly used devices produce ultrasound waves with frequencies either around 1-3 MHz or 20-150 kHz (known as long wavelength ultrasound). Similar effects by either 1-3 MHz or 45 kHz ultrasound waves on cells and tissues were reported in several studies [85,86]. The majority of ultrasound for physiotherapy uses frequencies in the range of 1-3 MHz, which traditionally is thought to produce less cavitation and thus less tissue damage. However, more recent laboratory findings indicate that the low frequency (20 to 100 KHz) ultrasound seems to produce a stronger biological impact [82,83,87,88], and at the same time seems to produce no cell or tissue damage [87,89,90]. With the availability of efficient low frequency ultrasound devices [91], low frequency ultrasound has found suitable application in several medical procedures [82-84].
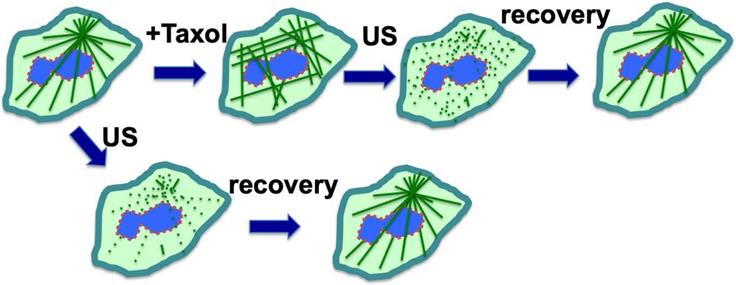
A serendipitous discovery is that ultrasound can eliminate paclitaxel cytotoxicity in cells. Although exposure to low intensity ultrasound (1 W/cm2) alone, for up to 10 minutes, had no noticeable impact on cultured cells, it actually reversed the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel in cancer cells [81]. Ultrasound at low intensity can disrupt microtubule cytoskeleton transiently without significant impact on cell survival [92,93]. For cells in culture, paclitaxel/Taxol treatment resulted in the appearance of strong staining of microtubule filaments, which was abolished by low intensity ultrasound (Fig. 4) [81]. After treatment with ultrasound and recovery, the microtubule cytoskeleton appeared to have the same morphology in paclitaxel-treated cells as those without paclitaxel treatment (Fig. 4A), but the ultrasound exposure completely eliminated paclitaxel cytotoxicity (Fig. 4) [81]. The finding was repeated and confirmed in various cell types, and it was concluded that low intensity ultrasound is capable of eliminating paclitaxel induced cytotoxicity in all cell types tested, by transiently breaking the rigid microtubule filaments [81] (Fig. 4).
Based on these results, a concept was developed that ultrasound reverses cytotoxicity by disrupting rigid microtubule filaments induced by paclitaxel treatment of proliferative cells (Fig 4) [81]. The physical breakage of paclitaxel-bound microtubules by ultrasound shock waves will result in the relocation of paclitaxel-bound microtubule fragments or tubulin heterodimers to lysosomes for degradation, and new microtubule networks will form rapidly from tubulins not bound to paclitaxel [81]. Tubulin levels in cells are auto-regulated, and newly synthesized tubulins quickly replace degraded paclitaxel-bound tubulins to form the microtubule cytoskeleton [49,51,94]. Thus, a brief pulse exposure to ultrasound efficiently removes the negative impact of paclitaxel on microtubule dynamics and cell cytotoxicity (Fig. 4).
A potential strategy is to reverse the early step of paclitaxel cytotoxicity by disrupting the rigid microtubule filaments induced by paclitaxel with low intensity ultrasound. Thus, the strategy may be successful to counter paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy at an early step, regardless of the complex down-stream mechanisms by which paclitaxel induces peripheral neuropathy.
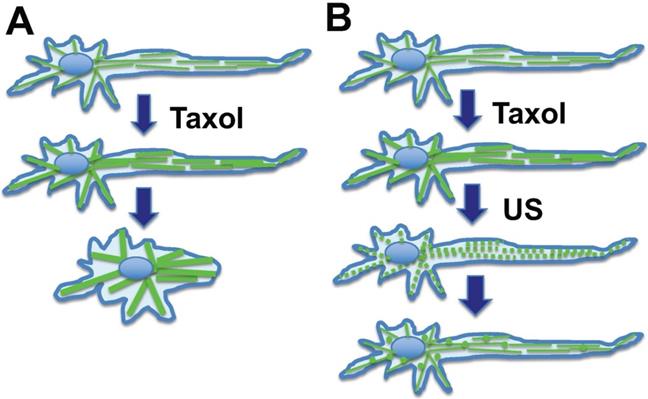
In chemotherapy, paclitaxel also causes stabilization and bundling of microtubules in peripheral neuronal cells, and consequently leads to retraction (Fig. 5A). This may reflect the underlying issue in peripheral neuropathy, which is thought to be caused by the impact of paclitaxel on the dynamics of the axonal long microtubule structure, presumably altering the distribution and structure of the peripheral neuron network and the transmission of nerve stimuli [63,95]. Low intensity ultrasound transiently disrupts the paclitaxel-induced rigid microtubule bundles (Fig. 5B). The paclitaxel bound microtubule fragments undergo lysosomal degradation. Additionally, paclitaxel is rapidly (8-24 hours) eliminated in the environment by binding to and being sequestered by cellular microtubules (about 10-20 µM in cells) [38,39,42], or bound by other cellular components. Increased synthesis of tubulins likely also contributes to paclitaxel elimination.
8. Potential prevention of taxane chemotherapy side effects using low intensity ultrasound
Low density ultrasound has been explored to influence peripheral neurons [96] or treat pain and neuropathy in clinical trials [97]; however, the current concept is based on a new discovery that ultrasound can eliminate acute paclitaxel cytotoxicity by breaking the rigid microtubules. While low intensity ultrasound has been extensively used for various medical applications [83,84], and laboratory studies show that ultrasound waves impact cells and may have biological activity even on hair follicles [98], the evidence to support medical applications of ultrasound is largely anecdotal. Most medical applications of ultrasound physiotherapies were determined to lack true merit in large and rigorous clinical studies [83,84]. Instead, the surprising findings [81] and unique hypothesis discussed here may be possible to introduce a rational, evidence-based use of ultrasound therapy for overcoming paclitaxel cytotoxicity into medical practice.
Ultrasound exposure reverses cytotoxicity by disrupting rigid microtubule filaments induced by paclitaxel (Taxol) treatment of cells. Microtubule bundles radiate out from the microtubule organizing center. Ultrasound (US) is known to transiently disrupt microtubule networks, which reform within 1-2 hours. Paclitaxel (Taxol) induces rigid microtubule filaments that lead to growth arrest and subsequent cell death in proliferative cells such as cancer cells or matrix keratinocytes of the hair follicles. We suggest a mechanism through which ultrasound reverses cytotoxicity by disrupting rigid microtubule filaments induced by paclitaxel. The paclitaxel-bound microtubule fragments and tubulins are relocated to lysosomes for degradation, and newly synthesized tubulins form a new network of microtubule cytoskeleton without bound paclitaxel. Thus, a brief exposure to low intensity ultrasound removes cellular paclitaxel activity/cytotoxicity.
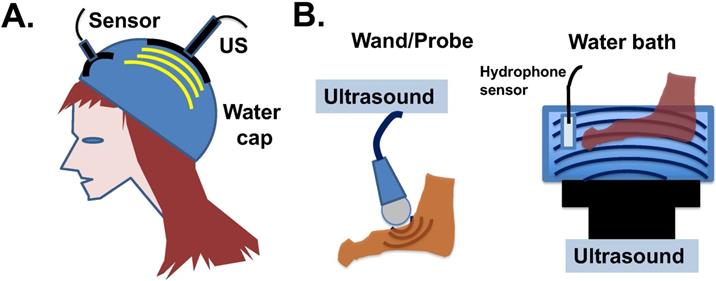
Since ultrasound treatment is considered a safe procedure, potential clinical development is eminently feasible. Ultrasound devices suitable to apply low intensity shock waves to the skin surface and hair follicles may be designed, and water may be suitable to be used as an ultrasound-transmitting medium (Fig. 6A). The human scalp is a strong barrier for the penetration of low frequency ultrasound energy [84], which actually eases the potential concern that the ultrasound waves may affect human brain. The application of ultrasound to hands, feet, and scalp a few hours after drug administration may be able to eliminate the persistent activity of paclitaxel already bound to the microtubules of the cells. Both the water bath and probe types of ultrasound devices can be considered for clinical application (Fig. 6B). The bath device produces 45-150 kHz, 1-3 W/cm2 ultrasound waves with adjustable frequency and energy levels. The probe device produces adjustable 1-3 W/cm2 and 1-3 MHz ultrasound waves.
Hypothesis: Ultrasound reverses neurite retraction by disrupting rigid microtubule filaments induced by paclitaxel. Axon maintenance in peripheral neuronal cells depends on microtubule dynamics. (A) Taxol/paclitaxel stabilizes microtubules and leads to neurite retraction. This may model the underlying issue of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. (B) Ultrasound (US) is known to disrupt the microtubule network, which in turn reforms rapidly. A mechanism is suggested that ultrasound disrupts paclitaxel-induced rigid microtubule bundles, leading to prevention of neurite retraction, and this concept may be explored to prevent paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Potential application of ultrasound devices for physiotherapy to prevent paclitaxel side effects in chemotherapy. (A) Illustration of ultrasound design to counter cytotoxicity in hair follicles of cancer patients undergoing paclitaxel (Taxol) treatment. A water-filled bag/cap is used to couple the transfer of ultrasound energy to epidermal and hair follicles under the wetted hair. Ultrasound intensity will be monitored (and potentially feedback regulated) by a built-in hydrophone sensor. (B) Illustration of two available devises for the transmission of ultrasound waves through water to peripheral tissues. The water bath ultrasound device gives out 45 kHz ultrasound shock wave with 1 to 3 W/cm2 energy, and the probe ultrasound device produces 1 to 3 MHz ultrasound in 1 to 3 W/cm2 energy waves.
Timing of ultrasound application for physiotherapy to prevent paclitaxel side effects in chemotherapy. During chemotherapy, paclitaxel (Taxol) is administrated to patients over 3-6 hours, and taxane concentration reaches a peak level in plasma by the end of drug infusion. Paclitaxel plasma levels fall rapidly following infusion over next 6 to 10 hours. It is reasoned that intermittent ultrasound (US) pulse treatment (5 min exposure) over a period of 4-10 hours may be suitable, when plasma drug levels are much lower. A second ultrasound treatment at around 24 hours may also helpful to further eliminate paclitaxel cytotoxicity locally at hands, feet, and scalp.
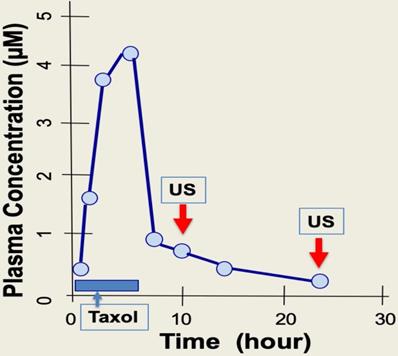
Paclitaxel is administrated through IV over a 4- to 6-hour time course. Upon completion of drug infusion, blood paclitaxel rapidly declines, and the drug enters and accumulates within cells [8,35,42]. The cellular level of paclitaxel is concentrated several hundred-fold higher than in blood, partly due to binding to cellular microtubules [8,35,37]. A short exposure of cells to paclitaxel leads to persistent cytotoxicity over several days even when extracellular sources of paclitaxel is absent, as the paclitaxel bound rigid microtubule bundles are present several days after [41]. During the 2-7 days after paclitaxel administration, the drug triggers death of cancer cells, but also causes damage to peripheral neurons that presents as peripheral neuropathy, and also to hair matrix keratinocytes that results in alopecia [14]. Thus, for a 3- to 6-hour infusion of paclitaxel, it may be suitable to treat patients with intermittent, low intensity ultrasound pulse therapy (5 min, about 1 W/cm2) over just a few hours (e.g. 4 to 10 hours) following chemotherapy (Fig. 7). Possibly, a second ultrasound treatment may be applied 24 hours after chemotherapy to ensure complete localized elimination of paclitaxel cytotoxicity (e.g., in scalp skin but not in cancer cells) (Fig. 7). The optimal timing of ultrasound exposure to reverse paclitaxel activity may be the window between the time when free paclitaxel is depleted, and the time required for causing damage and harm by the paclitaxel-bound rigid microtubules (Fig. 7). Thus, ultrasound treatment appears to disrupt the persistent paclitaxel-bound rigid microtubules and thereby eliminate the prolonged cytotoxicity of paclitaxel.
Newer microtubule stabilizing drugs and delivering platforms, such as Abraxanes, cabazitaxel, epothilones (ixabepilone), laulimalide, and discodermolide, etc., are under development and coming into clinical application [99-104]. These new agents act with a mechanism same as paclitaxel, the first generation of microtubule stabilizing drugs, with similar side effects. Similarly, low intensity ultrasound likely will disrupt microtubules affected by these new drugs in the same way the ultrasound acts on paclitaxel-induced rigid microtubule bundles. Thus, ultrasound treatment may also relieve side effects from the new microtubule stabilizing drugs.
The application of ultrasound to counter paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy seems to be very feasible and practical. In fact, probe ultrasound has been used in clinical trials to treat paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy [97]. However, the current research findings suggest that ultrasound may prevent, but not reverse paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy and alopecia, and this will be a new rationale based on a solid scientific basis.
9. Summary
Paclitaxel (and other taxane drugs) binds and stabilizes microtubules, while ultrasound breaks microtubules, thus acting as an antidote. The mechanism may be quite self-explanatory. Based on our recent discovery that low intensity ultrasound treatment can effectively and almost completely neutralize the cytotoxic effects of paclitaxel in various cell types, a strategy may be developed to counter the side effects of paclitaxel-based chemotherapy for cancer patients. The concept that a brief exposure of paclitaxel-treated cells to ultrasound is sufficient to break paclitaxel-induced rigid microtubules opens up the possibility to use ultrasound locally to eliminate cytotoxicity at only the desirable anatomic sites, without affecting paclitaxel activity towards neoplastic cells. In essence, ultrasound is able to remove the persistent activity of paclitaxel at intended areas after systematic drug infusion. The possibilities to use this paclitaxel antidote can be contemplated to prevent chemotherapy-induced alopecia, and peripheral neuropathy, which will ensure the full use of paclitaxel dosage in treatment and improve the quality of life for cancer patients.
Acknowledgements
We thank our lab members and alumni for the research work supporting this review/opinion paper. We acknowledge that many additional excellent works and publications are relevant to the discussed topic, but are not cited due to the limited scope of this review/opinion manuscript.
Funding
This work from our lab discussed and cited was supported by funds from grant NICHD R03HD071244 (E.R.S.), concept awards BC097189 and BC076832 from Department of Defense (USA). Grants R01 CA230916, R01 CA095071, R01 CA099471, and CA79716 to X-X Xu from NCI, NIH also contributed to the studies. Internal research funding from the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center and University of Miami also supported this work.
Competing Interests
The authors declared no competing interests.
References
1. Gallego-Jara J, Lozano-Terol G, Sola-Martínez RA, Cánovas-Díaz M, de Diego Puente T. A compressive review about taxol: History and future challenges. Molecules. 2020;25(24):5986
2. Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. Paclitaxel (taxol). N Engl J Med. 1995Apr13;332(15):1004-1014
3. Baird RD, Tan DS, Kaye SB. Weekly paclitaxel in the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010Oct;7(10):575-582
4. Baker KG, Robertson VJ, Duck FA. A Review of Therapeutic Ultrasound: Biophysical Effects. Physical Therapy. 2001;81(7):1351-1358
5. Jain A, Dubashi B, Reddy KS, Jain P. Weekly paclitaxel in ovarian cancer-the latest success story. Curr Oncol. 2011Jan;18(1):16-17
6. Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979;277(5698):665-667
7. Schiff PB, Horwitz SB. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980Mar;77(3):1561-1565
8. Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:253-265
9. Horwitz SB. Taxol (paclitaxel): mechanisms of action. Ann Oncol. 1994;5(Suppl 6):S3-6
10. Weaver BA. How Taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25(18):2677-2681
11. Morse DL, Gray H, Payne CM, Gillies RJ. Docetaxel induces cell death through mitotic catastrophe in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1495-1504
12. Canta A, Chiorazzi A, Cavaletti G. Tubulin: a target for antineoplastic drugs into the cancer cells but also in the peripheral nervous system. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16:1315-1324
13. Paus R, Haslam IS, Sharov AA, Botchkarev VA. Pathobiology of chemotherapy-induced hair loss. Lancet Oncol. 2013Feb;14(2):e50-59
14. Purba TS, Ng'andu K, Brunken L, Smart E, Mitchell E, Hassan N, O'Brien A, Mellor C, Jackson J, Shahmalak A, Paus R. CDK4/6 inhibition mitigates stem cell damage in a novel model for taxane-induced alopecia. EMBO Mol Med. 2019Oct;11(10):e11031
15. Rowinsky EK, Eisenhauer EA, Chaudhry V, Arbuck SG, Donehower RC. Clinical toxicities encountered with paclitaxel (Taxol). Semin Oncol. 1993;20(4 Suppl 3):1-15
16. Blagosklonny MV, Fojo T. Molecular effects of paclitaxel: myths and reality (a critical review). Int J Cancer. 1999Oct8;83(2):151-156
17. Wani MC, Horwitz SB. Nature as a remarkable chemist: a personal story of the discovery and development of Taxol. Anticancer Drugs. 2014;25(5):482-487
18. Jordan MA. Mechanism of action of antitumor drugs that interact with microtubules and tubulin. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2002;2(1):1-17
19. Mitchison TJ, Pineda J, Shi J, Florian S. Is inflammatory micronucleation the key to a successful anti-mitotic cancer drug? Open Biol. 2017;7(11):170182
20. Komlodi-Pasztor E, Sackett D, Wilkerson J, Fojo T. Mitosis is not a key target of microtubule agents in patient tumors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8(4):244-250
21. Komlodi-Pasztor E, Sackett DL, Fojo AT. Inhibitors targeting mitosis: tales of how great drugs against a promising target were brought down by a flawed rationale. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(1):51-63
22. Mitchison TJ. The proliferation rate paradox in antimitotic chemotherapy. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:1-6
23. Fürst R, Vollmar AM. A new perspective on old drugs: non-mitotic actions of tubulin-binding drugs play a major role in cancer treatment. Pharmazie. 2013;68:478-483
24. Smith ER, Xu XX. Breaking malignant nuclei as a non-mitotic mechanism of taxol/paclitaxel. J Cancer Biol. 2021;2(4):86-93
25. Smith ER, Leal J, Amaya C, Li B, Xu XX. Nuclear Lamin A/C Expression Is a Key Determinant of Paclitaxel Sensitivity. Mol Cell Biol. 2021Jun23;41(7):e0064820
26. Capo-chichi CD, Cai KQ, Simpkins F, Ganjei-Azar P, Godwin AK, Xu XX. Nuclear envelope structural defects cause chromosomal numerical instability and aneuploidy in ovarian cancer. BMC Med. 2011;9:28
27. Capo-Chichi CD, Yeasky TM, Smith ER, Xu XX. Nuclear envelope structural defect underlies the main cause of aneuploidy in ovarian carcinogenesis. BMC Cell Biol. 2016;17:37
28. Smith ER, Capo-Chichi CD, Xu XX. Defective Nuclear Lamina in Aneuploidy and Carcinogenesis. Front Oncol. 2018;8:529
29. Smith ER, George SH, Kobetz E, Xu XX. New biological research and understanding of Papanicolaou's test. Diagn Cytopathol. 2018;46:507-515
30. Niu N, Zhang J, Zhang N, Mercado-Uribe I, Tao F, Han Z, Pathak S, Multani AS, Kuang J, Yao J, Bast RC, Sood AK, Hung MC, Liu J. Linking genomic reorganization to tumor initiation via the giant cell cycle. Oncogenesis. 2016Dec19;5(12):e281
31. Niu N, Mercado-Uribe I, Liu J. Dedifferentiation into blastomere-like cancer stem cells via formation of polyploid giant cancer cells. Oncogene. 2017Aug24;36(34):4887-4900
32. Niu N, Yao J, Bast RC, Sood AK, Liu J. IL-6 promotes drug resistance through formation of polyploid giant cancer cells and stromal fibroblast reprogramming. Oncogenesis. 2021Sep29;10(9):65
33. Liu J, Niu N, Li X, Zhang X, Sood AK. The life cycle of polyploid giant cancer cells and dormancy in cancer: Opportunities for novel therapeutic interventions. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021Oct;17:S1044-579X (21)00255-8
34. Merlin JL, Bour-Dill C, Marchal S, Bastien L, Gramain MP. Resistance to paclitaxel induces time-delayed multinucleation and DNA fragmentation into large fragments in MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2000Apr;11(4):295-302
35. Wiernik PH, Schwartz EL, Strauman JJ, Dutcher JP, Lipton RB, Paietta E. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of taxol. Cancer Res. 1987May1;47(9):2486-2493
36. Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. The clinical pharmacology of paclitaxel (Taxol). Semin Oncol. 1993Aug;20(4 Suppl 3):16-25
37. Manfredi JJ, Parness J, Horwitz SB. Taxol binds to cellular microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1982Sep;94(3):688-696
38. Cassimeris L, Silva VC, Miller E, Ton Q, Molnar C, Fong J. Fueled by Microtubules: Does Tubulin Dimer/Polymer Partitioning Regulate Intracellular Metabolism? Cytoskeleton. 2012;69:133-143
39. Zhai Y, Borisy GG. Quantitative determination of the proportion of microtubule polymer present during the mitosis-interphase transition. J Cell Sci. 1994;107:881-890
40. Michalakis J, Georgatos SD, de Bree E, Polioudaki H, Romanos J, Georgoulias V, Tsiftsis DD, Theodoropoulos PA. Short-term exposure of cancer cells to micromolar doses of paclitaxel, with or without hyperthermia, induces long-term inhibition of cell proliferation and cell death in vitro. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007Mar;14(3):1220-1228
41. Mori T, Kinoshita Y, Watanabe A, Yamaguchi T, Hosokawa K, Honjo H. Retention of paclitaxel in cancer cells for 1 week in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006Nov;58(5):665-672
42. Koshiba H, Hosokawa K, Mori T, Kubo A, Watanabe A, Honjo H. Intravenous paclitaxel is specifically retained in human gynecologic carcinoma tissues in vivo. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009May;19(4):484-488
43. Desai A, Mitchison TJ. MICROTUBULE POLYMERIZATION DYNAMICS. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:83-117
44. Baas PW. Microtubules and axonal growth. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:29-36
45. Diaz JF, Andreu JM. Assembly of purified GDP-tubulin into microtubules induced by taxol and taxotere: reversibility, ligand stoichiometry, and competition. Biochemistry. 1993;32:2747-2755
46. Holmfeldt P, Sellin ME, Gullberg M. Predominant regulators of tubulin monomer-polymer partitioning and their implication for cell polarization. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:3263-3276
47. Huff LM, Sackett DL, Poruchynsky MS, Fojo T. Microtubule-disrupting chemotherapeutics result in enhanced proteasome-mediated degradation and disappearance of tubulin in neural cells. Cancer Res. 2010Jul15;70(14):5870-5879
48. Johnson GV, Litersky JM, Whitaker JN. Proteolysis of microtubule-associated protein 2 and tubulin by cathepsin D. J Neurochem. 1991Nov;57(5):1577-1583
49. Caron JM, Jones AL, Kirschner MW. Autoregulation of tubulin synthesis in hepatocytes and fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1985;101:1763-1772
50. Laferriere NB, MacRae TH, Brown DL. Tubulin synthesis and assembly in differentiating neurons. Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;75:103-117
51. Lin Z, Gasic I, Chandrasekaran V, Peters N, Shao S, Mitchison TJ, Hegde RS. TTC5 mediates autoregulation of tubulin via mRNA degradation. Science. 2020Jan3;367(6473):100-104
52. Rossi A, Fortuna MC, Caro G, Pranteda G, Garelli V, Pompili U, Carlesimo M. Chemotherapy-induced alopecia management: Clinical experience and practical advice. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017;16:537-541
53. Paus R, Cotsarelis G. The biology of hair follicles. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:491-497
54. Botchkarev VA, Paus R. Molecular biology of hair morphogenesis: development and cycling. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2003Aug15;298(1):164-180
55. Freites-Martinez A, Chan D, Sibaud V, Shapiro J, Fabbrocini G, Tosti A, Cho J, Goldfarb S, Modi S, Gajria D, Norton L, Paus R, Cigler T, Lacouture ME. Assessment of Quality of Life and Treatment Outcomes of Patients With Persistent Postchemotherapy Alopecia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019Jun1;155(6):724-728
56. Kudlowitz D, Muggia F. Clinical features of taxane neuropathy. Anticancer Drugs. 2014;25:495-501
57. Mielke S, Sparreboom A, Mross K. Peripheral neuropathy: a persisting challenge in paclitaxel-based regimes. Eur J Cancer. 2006Jan;42(1):24-30
58. Malacrida A, Meregalli C, Rodriguez-Menendez V, Nicolini G. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Changes in Cytoskeleton. Int J Mol Sci. 2019May9;20(9):2287
59. Boyette-Davis JA, Cata JP, Driver LC, Novy DM, Bruel BM, Mooring DL, Wendelschafer-Crabb G, Kennedy WR, Dougherty PM. Persistent chemoneuropathy in patients receiving the plant alkaloids paclitaxel and vincristine. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013Mar;71(3):619-626
60. Velasco R, Bruna J. Taxane-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity. Toxics. 2015;3(2):152-169
61. Cirrincione AM, Rieger S. Analyzing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in vivo using non-mammalian animal models. Exp Neurol. 2020Jan;323:113090
62. Cirrincione AM, Pellegrini AD, Dominy JR, Benjamin ME, Utkina-Sosunova I, Lotti F, Jergova S, Sagen J, Rieger S. Paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy is caused by epidermal ROS and mitochondrial damage through conserved MMP-13 activation. Sci Rep. 2020Mar4;10(1):3970
63. Staff NP, Fehrenbacher JC, Caillaud M, Damaj MI, Segal RA, Rieger S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp Neurol. 2020Feb;324:113121
64. Kawashiri T, Inoue M, Mori K, Kobayashi D, Mine K, Ushio S, Kudamatsu H, Uchida M, Egashira N, Shimazoe T. Preclinical and Clinical Evidence of Therapeutic Agents for Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:8733
65. Abal M, Andreu JM, Barasoain I. Taxanes: microtubule and centrosome targets, and cell cycle dependent mechanisms of action. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3(3):193-203
66. DiRocco DP, Bisi J, Roberts P, Strum J, Wong KK, Sharpless N, Humphreys BD. CDK4/6 inhibition induces epithelial cell cycle arrest and ameliorates acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014Feb15;306(4):F379-388
67. Pabla N, Gibson AA, Buege M, Ong SS, Li L, Hu S, Du G, Sprowl JA, Vasilyeva A, Janke LJ, Schlatter E, Chen T, Ciarimboli G, Sparreboom A. Mitigation of acute kidney injury by cell-cycle inhibitors that suppress both CDK4/6 and OCT2 functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015Apr21;112(16):5231-5236
68. He S, Roberts PJ, Sorrentino JA, Bisi JE, Storrie-White H, Tiessen RG, Makhuli KM, Wargin WA, Tadema H, van Hoogdalem EJ, Strum JC, Malik R, Sharpless NE. Transient CDK4/6 inhibition protects hematopoietic stem cells from chemotherapy-induced exhaustion. Sci Transl Med. 2017Apr26;9(387):eaal3986
69. Lasheen S, Shohdy KS, Kassem L, Abdel-Rahman O. Fatigue, alopecia and stomatitis among patients with breast cancer receiving cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017Sep;17(9):851-856
70. Yang L, Xue J, Yang Z, Wang M, Yang P, Dong Y, He X, Bao G, Peng S. Side effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Palliat Med. 2021May;10(5):5590-5599
71. Zhang M, Zhang L, Hei R, Li X, Cai H, Wu X, Zheng Q, Cai C. CDK inhibitors in cancer therapy, an overview of recent development. Am J Cancer Res. 2021May15;11(5):1913-1935
72. Fukuda Y, Li Y, Segal RA. A mechanistic understanding of axon degeneration in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2017;11:481
73. Polomano RC, Mannes AJ, Clark US, Bennett GJ. A painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat produced by the chemotherapeutic drug, paclitaxel. Pain. 2001Dec;94(3):293-304
74. Flatters SJL, Bennett GJ. Studies of peripheral sensory nerves in paclitaxel-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction. Pain. 2006Jun;122(3):245-257
75. Lisse TS, Middleton LJ, Pellegrini AD, Martin PB, Spaulding EL, Lopes O, Brochu EA, Carter EV, Waldron A, Rieger S. Paclitaxel-induced epithelial damage and ectopic MMP-13 expression promotes neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016Apr12;113(15):E2189-198
76. Griffiths C, Kwon N, Beaumont JL, Paice JA. Cold therapy to prevent paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Support Care Cancer. 2018Oct;26(10):3461-3469
77. Hanai A, Ishiguro H, Sozu T, Tsuda M, Yano I, Nakagawa T, Imai S, Hamabe Y, Toi M, Arai H, Tsuboyama T. Effects of Cryotherapy on Objective and Subjective Symptoms of Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathy: Prospective Self-Controlled Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018Feb1;110(2):141-148
78. Rice BA, Ver Hoeve ES, DeLuca AN, Esserman LJ, Rugo HS, Melisko ME. Registry study to assess hair loss prevention with the Penguin Cold Cap in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018Jan;167(1):117-122
79. van den Hurk CJ, Peerbooms M, van de Poll-Franse LV, Nortier JW, Coebergh JW, Breed WP. Scalp cooling for hair preservation and associated characteristics in 1411 chemotherapy patients - results of the Dutch Scalp Cooling Registry. Acta Oncol. 2012Apr;51(4):497-504
80. Wang S, Yang T, Shen A, Qiang W, Zhao Z, Zhang F. The scalp cooling therapy for hair loss in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer. 2021Nov;29(11):6943-6956
81. Amaya C, Luo S, Baigorri J, Baucells R, Smith ER, Xu XX. Exposure to low intensity ultrasound removes paclitaxel cytotoxicity in breast and ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2021Sep1;21(1):981
82. Abramavičius S, Volkevičiūtė A, Tunaitytė A, Venslauskas M, Bubulis A, Bajoriūnas V, Stankevičius E. Low-Frequency (20 kHz) Ultrasonic Modulation of Drug Action. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020Nov;46(11):3017-331
83. Ahmadi F, McLoughlin IV, Chauhan S, ter-Haar G. Bio-effects and safety of low-intensity, low-frequency ultrasonic exposure. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012;108(3):119-138
84. ter Haar G. Therapeutic applications of ultrasound. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007;93(1-3):111-129
85. Reher P, Doan N, Bradnock B, Meghji S, Harris M. Therapeutic ultrasound for osteoradionecrosis: an in vitro comparison between 1 MHz and 45 kHz machines. Eur J Cancer. 1998Nov;34(12):1962-1968
86. Robertson VJ, Ward AR. Subaqueous ultrasound: 45kHz and 1MHz machines compared. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995Jun;76(6):569-575
87. Iida K, Luo H, Hagisawa K, Akima T, Shah PK, Naqvi TZ, Siegel RJ. Noninvasive low-frequency ultrasound energy causes vasodilation in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:532-537
88. Samuels JA, Weingarten MS, Margolis DJ, Zubkov L, Sunny Y, Bawiec CR, Conover D, Lewin PA. Low-frequency (<100 kHz), low-intensity (<100 mW/cm(2)) ultrasound to treat venous ulcers: a human study and in vitro experiments. J Acoust Soc Am. 2013Aug;134(2):1541-1547
89. Fischell TA, Abbas MA, Grant GW, Siegel RJ. Ultrasonic energy. Effects on vascular function and integrity. Circulation. 1991Oct;84(4):1783-1795
90. Scarponi C, Nasorri F, Pavani F, Madonna S, Sestito R, Simonacci M, De Pità O, Cavani A, Albanesi C. Low-frequency low-intensity ultrasounds do not influence the survival and immune functions of cultured keratinocytes and dendritic cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009;2009:193260
91. Sunny Y, Bawiec CR, Nguyen AT, Samuels JA, Weingarten MS, Zubkov LA, Lewin PA. Optimization of un-tethered, low voltage, 20-100kHz flexural transducers for biomedical ultrasonics applications. Ultrasonics. 2012Sep;52(7):943-948
92. Adler J, Necas O, Hrazdira I. Dissassembly of microtubules due to low intensity ultrasound. Folia Biol. (Praha). 1993;39:55-57
93. Samandari M, Abrinia K, Mokhtari-Dizaji M, Tamayol A. Ultrasound induced strain cytoskeleton rearrangement: An experimental and simulation study. J Biomech. 2017;60:39-47
94. Gasic I, Boswell SA, Mitchison TJ. Tubulin mRNA stability is sensitive to change in microtubule dynamics caused by multiple physiological and toxic cues. PLoS Biol. 2019;17(4):e3000225
95. Gornstein E, Schwarz TL. The paradox of paclitaxel neurotoxicity: Mechanisms and unanswered questions. Neuropharmacology. 2014 76 Pt A:175-183
96. Jiang W, Wang Y, Tang J, Peng J, Wang Y, Guo Q, Guo Z, Li P, Xiao B, Zhang J. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound treatment improved the rate of autograft peripheral nerve regeneration in rat. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22773
97. Al Onazi MM, Yurick JL, Harris C, Nishimura K, Suderman K, Pituskin E, Chua N, McNeely ML. Therapeutic Ultrasound for Chemotherapy-Related Pain and Sensory Disturbance in the Hands and Feet in Patients With Colorectal Cancer: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2021Jun;61(6):1127-1138
98. Liao AH, Lin KH, Chuang HC, Tsai CH, Lin YC, Wang CH, Shih CP, Liu HL. Low-frequency dual-frequency ultrasound-mediated microbubble cavitation for transdermal minoxidil delivery and hair growth enhancement. Sci Rep. 2020Mar9;10(1):4338
99. Altaha R, Fojo T, Reed E. Abraham Epothilones: a novel class of non-taxane microtubule-stabilizing agents. J Curr Pharm Des. 2002;8(19):1707-1712
100. Cao YN, Zheng LL, Wang D, Liang XX, Gao F, Zhou XL. Recent advances in microtubule-stabilizing agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;143:806-828
101. Hunt JT. Discovery of ixabepilone. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(2):275-281
102. Sofias AM, Dunne M, Storm G, Allen C. The battle of "nano" paclitaxel. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:20-30
103. Zhao Y, Mu X, Du G. Microtubule-stabilizing agents: New drug discovery and cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;162:134-143
104. Kundranda MN, Niu J. Albumin-bound paclitaxel in solid tumors: clinical development and future directions. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:3767-3777
Author contact
![]() Corresponding author: xxu2miami.edu
Corresponding author: xxu2miami.edu

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact