3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(7):2388-2396. doi:10.7150/jca.71526 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Wnt5a-mediated autophagy promotes radiation resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
1. The Affiliated Changsha Central Hospital, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China. Changsha, Hunan, 410001, People's Republic of China.
2. Changsha Aier Eye Hospital, Aier Eye Hospital Group, Changsha, Hunan,410000, People's Republic of China.
3. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, 87 Xiangya Road, Changsha, Hunan 410008, People's Republic of China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
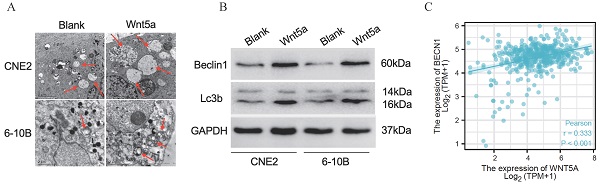
Wnt signaling pathways and autophagy play an essential role in tumor progression. Canonical Wnt signaling pathways in radiation resistance have been studied in the past, but it remains unclear whether the noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways can affect tumor radiation resistance through protective autophagy. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, a particular subtype of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, relies on radiation therapy. In this study, we found that radioactive rays could significantly promote the expression of Wnt noncanonical signaling pathways ligands in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, among which Wnt5A was the most markedly altered. We have demonstrated that Wnt5a can reduce the radiation sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vitro experiments. Meanwhile, we found much more greater autophagosomes in overexpressed-Wnt5A nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by electron microscopy. Further mechanism exploration revealed that Beclin1 is the main target of Wnt5A, and knocking down Beclin1 can partially reduce Wnt5a-induced radiation resistance. By studying Wnt5A-mediated protective autophagy in promoting radiation resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, we hope that the Wnt5A and Beclin1 can become effective targets for overcoming radiation resistance in the future.
Keywords: Wnt5a, autophagy, radiation resistance, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact