3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(9):2781-2797. doi:10.7150/jca.73690 This issue Cite
Research Paper
RELA-induced MiR-21 Exerts Oncogenic Effects on PDAC via Targeting of ARHGAP24
1. Department of Gastroenterology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 201620, China.
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Diseases, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 201620, China.
3. Department of Gastroenterology, Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200336, China.
#These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
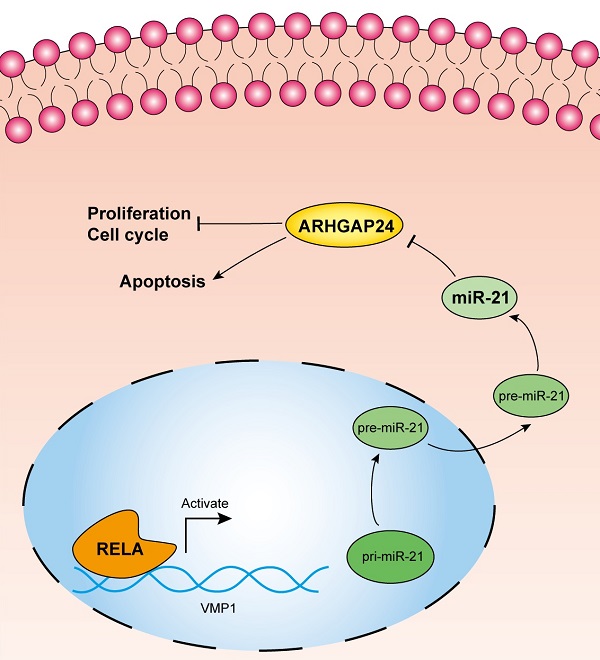
Inflammation is one of the inducing factors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and microRNAs have been confirmed to be involved in the occurrence and development of PDAC. However, whether RELA, an inflammatory regulator, is involved in the regulation of PDAC by miRNA remains to be further studied. In the present study miR-21 was characterized and its upstream regulatory mechanism was investigated, as well as its functional effects and target genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). In situ hybridization analysis confirmed increased miR-21 expression levels in PDAC tissues. The results of the chromatin immunoprecipitation and dual-luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that transcription factor RELA modulated miR-21 transcription in the PDAC, PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cell lines. Subsequently, a cell viability assay, EdU staining assay and flow cytometry analysis, demonstrated that miR-21 promoted cell proliferation and cell cycle progression, but inhibited cell apoptosis in vitro. Furthermore, a xenograft assay demonstrated that miR-21 accelerated tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistically, miR-21 directly regulated the expression of Rho GTPase activating protein 24 (ARHGAP24), which was indicated to be a tumor suppressor gene. Moreover, both miR-21 and ARHGAP24 were strongly associated with clinical features and may therefore serve as valuable biomarkers in PDAC prognosis.
Keywords: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, ARHGAP24, RELA, microRNA, Transcription factor

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact