3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(3):336-349. doi:10.7150/jca.79465 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Ferroptosis and Apoptosis Induction through P53 and GSK-3β/Nrf2 Signal Pathways using Qingrehuoxue Formula
1. Department of Geriatric Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 250014, Jinan, China.
2. First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, China.
3. College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, China.
4. Department of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, China.
5. Department of Integrative Medicine, Huashan Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
6. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
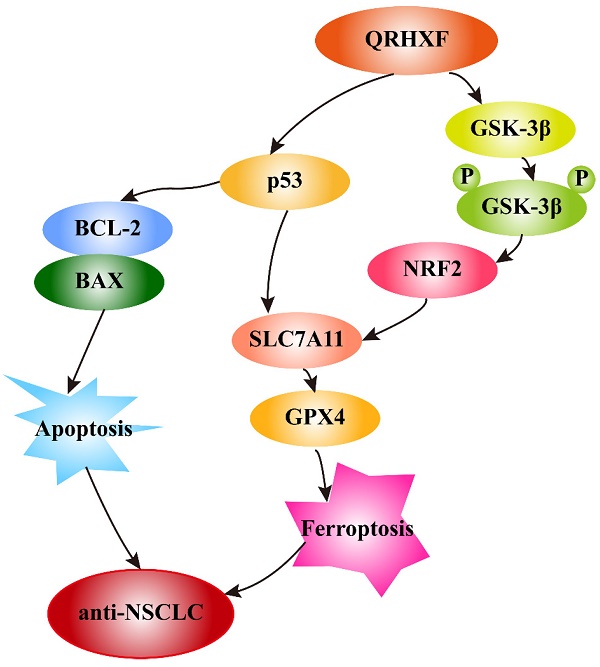
This study aimed to elucidate the effects of Qingrehuoxue Formula (QRHXF) on NSCLC and its underlying mechanisms. Nude mouse model of subcutaneous tumors was established. QRHXF and erastin were administered orally and intraperitoneally, respectively. Mice's body weight and subcutaneous tumor volumes were measured. The effects of QRHXF on epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), tumor-associated angiogenesis and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) were assessed. Importantly, we also analysed the anti-NSCLC of QRHXF form the aspect of ferroptosis and apoptosis and investigate its underlying mechanisms. The safety of QRHXF in mice was also evaluated. QRHXF slowed down the speed of tumor growth and visibly inhibited tumor growth. The expression levels of CD31, VEGFA, MMP2 and MMP9 were prominently suppressed by QRHXF. Furthermore, QRHXF appeared to remarkably inhibite cell proliferation and EMT by decreasing Ki67, N-cadherin and vimentin expression but elevating E-cadherin expression. There were more apoptotic cells in QRHXF group's tumor tissues, and QRHXF treatment increased BAX and cleaved-caspased 3 levels but decreased Bcl-2 levels. QRHXF significantly increased the accumulation of ROS, Fe2+, H2O2, and MDA while reduced GSH levels. SLC7A11 and GPX4 protein levels were considerably suppressed by QRHXF treatment. Moreover, QRHXF triggered ultrastructural changes in the mitochondria of tumor cells. The levels of p53 and p-GSK-3β were upregulated, whereas that of Nrf2 was downregulated in the groups treated with QRHXF. QRHXF displayed no toxicity in mice. QRHXF activated ferroptosis and apoptosis to suppress NSCLC cell progression via p53 and GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling pathways.
Keywords: Traditional Chinese Medicine, NSCLC, anti-tumor, mechanism, signal pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact