3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(4):544-553. doi:10.7150/jca.81793 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Visualizing intratumoral injections in lung tumors by endobronchial ultrasound
1. Vermont Lung Center, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Vermont College of Medicine, Burlington, VT 05405, USA.
2. Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Medicine, University of Vermont, Burlington VT 05405.
Abstract
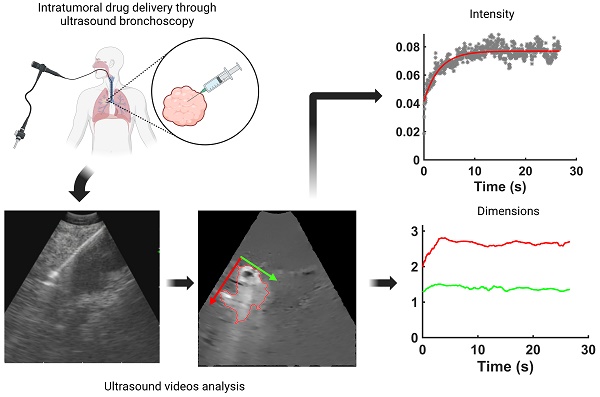
Real-time endobronchial ultrasound images are crucial for the accurate placement of the needle in peribronchial lung tumors and lymph nodes for diagnostic sampling. Beyond its role as a diagnostic tool, ultrasound-guided bronchoscopy can also aid the delivery of anti-cancer agents intratumorally, enabling diagnosis, staging, and treatment to occur within the same anesthesia, reducing the patient's burden. However, determining drug retention and distribution in situ remains challenging, albeit pivotal in assessing the success or failure of the therapeutic intervention. We hypothesized that ultrasound images acquired by the bronchoscope during the injection can provide qualitative and quantitative real-time information about drug transport. As a proof-of-concept, we retrospectively analyzed 13 videos of intratumoral cisplatin injections in advanced non-small cell lung cancers. We identified the injection and performed quantitative analysis through image processing and segmentation algorithms and mathematical models in 5 of them. We were able to infer the unlikeliness of a laminar flow through interstitial pores in favor of the emergence of tissue fractures. These data imply that the structural integrity of the tumor is a critical determinant of the ultimate distribution of an intratumorally delivered agent.
Keywords: EBUS-TBNI, Intratumoral Chemotherapy, Drug Dynamics

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact