Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(15):2784-2797. doi:10.7150/jca.86572 This issue Cite
Research Paper
RBMS3, a downstream target of AMPK, Exerts Inhibitory Effects on Invasion and Metastasis of Lung Cancer
1. Hospital of Gastroenterology, Institute of Digestive Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China.
2. Queen Mary university, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
3. Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Digestive, Cardiovascular, and Neurological Diseases of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China.
4. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China.
#These authors contributed equally to the work.
Abstract
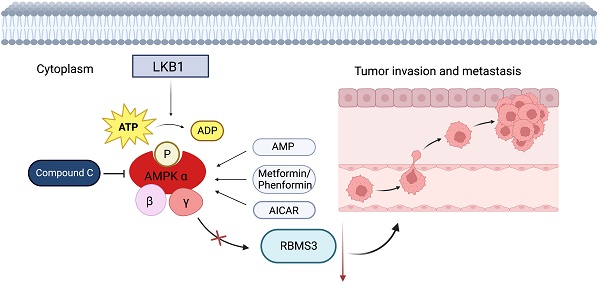
Background: Lung cancer is a highly malignant disease, primarily due to its propensity for metastasis. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), the principal downstream effector of Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1), orchestrates a broad spectrum of molecular targets, thereby constraining tumor invasion and metastasis. In parallel, the RNA-binding protein RBMS3 (RNA-binding motif, single-stranded-interacting protein 3) plays a pivotal role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a pivotal process in tumorigenesis. Therefore, our research aims to clarify the important role of RBMS3 as a mediator in the LKB1/AMPK inhibition of tumor invasion and metastasis.
Methods: We investigated the expression and correlation between RBMS3 and LKB1 in lung cancer tissues utilizing immunohistochemistry and TCGA-LUAD data, respectively. The relationship between RBMS3 and clinical pathological features and prognosis of lung cancer was also analyzed. The functions of RBMS3 in lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration were investigated in real-time in vitro. Additionally, we investigated the effects of AMPK agonists and inhibitors to explore the mediating role of RBMS3 in AMPK-induced inhibition of lung cancer invasion and migration.
Results: The IHC and TCGA data both revealed low expression of RBMS3 in lung cancer. Moreover, we found that low expression of RBMS3 was positively associated with lung cancer's histological grade, clinical stage, and N stage. Additionally, low RBMS3 expression was associated with poor overall survival. Cox regression analysis revealed that RBMS3 was an independent prognostic factor for lung cancer patients. In vitro experiments verified that RBMS3 inhibited lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. Furthermore, our findings suggested that RBMS3 played an essential role in mediating AMPK's inhibitory effect on lung cancer invasion and migration.
Conclusion: Our study highlights a novel mechanism by which LKB1/AMPK pathway activation inhibits lung cancer invasion and metastasis by promoting RBMS3 expression, offering insights in developing innovative lung cancer therapies.
Keywords: AMPK, RBMS3, lung cancer, invasion and metastasis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact