3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(16):3130-3138. doi:10.7150/jca.84484 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Role of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University/Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China.
2. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Cancer Institute and Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, BeiJing, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods: This retrospective study included patients diagnosed with ESCC at clinical stage T1N1-3M0 or T2-4N0-3M0. Six hundred and eleven patients underwent radical tumor surgical resection after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Adjuvant chemotherapy was mainly a platinum-based combination regimen. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to compare adjuvant chemotherapy (AC) vs. postoperative observation (POB) after surgery.
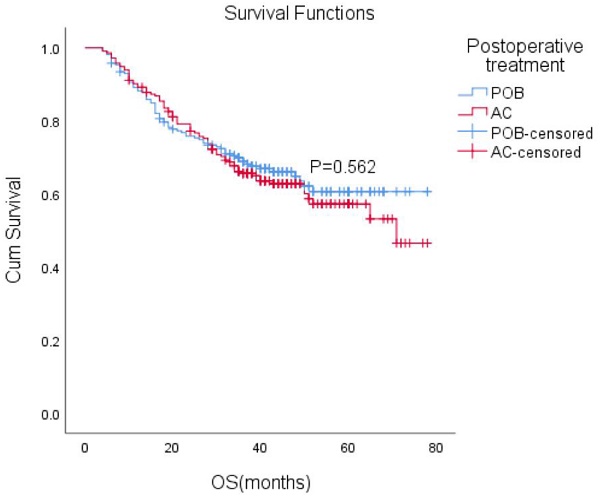
Results: A total of 611 patients were eligible, with 381 in the POB group and 230 in the AC group. POB group patients were younger (P=0.046) and at a later stage (ypT3/4: 127 [55%] vs. 177 [46%]), P=0.036; yPN+: 117[51%] vs. 3428[37%], P=0.001) before PSM. After 1:1 PSM, 213 pairs of patients were included in analysis. The 5-year overall survival (OS) was 60.6% and 57.2% in the POB and AC groups, respectively (HR 1.10, 95% CI: 0.80-1.51, P=0.562), and adjuvant chemotherapy did not improve OS compared with postoperative observation.
Conclusions: Postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy cannot improve the OS of patients with ESCC after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, but adjuvant chemotherapy tends to benefit ypN+ patients.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, adjuvant chemotherapy, survival, prognosis.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact