3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(1):232-250. doi:10.7150/jca.87733 This issue Cite
Research Paper
IGFBP5, as a Prognostic Indicator Promotes Tumor Progression and Correlates with Immune Microenvironment in Glioma
1. Central laboratory, Cancer Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong 515041, China.
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment, Cancer Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong 515041, China.
3. Department of Pathology, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong, 515041, China.
4. The Breast Center, Surgical Oncology Session No. 1, Cancer Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong 515041, China.
5. Department of Pathology, Shantou Central Hospital, Shantou, Guangdong 515041, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) is highly expressed in multiple human cancers, including glioma. Despite this, it remains unclear what role it plays in glioma. The aim of the present study was to analyze whether IGFBP5 could be used as a predictor of prognosis and immune infiltration in glioma.
Methods: Glioma patients' clinical information was collected from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA), Rembrandt, and Gravendeel databases. The diagnostic and prognostic roles of IGFBP5 were assessed by the Kaplan-Meier survival curves, diagnostic receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, nomogram model, Cox regression analysis and Enrichment analysis by R software. Moreover, the correlation between IGFBP5 expression and immune cell infiltration, and immune checkpoint genes was conducted. Immunohistochemistry staining, CCK8, colony formation, scratch and transwell assays and western blot were used to interrogate the expression and function of IGFBP5 in glioma.
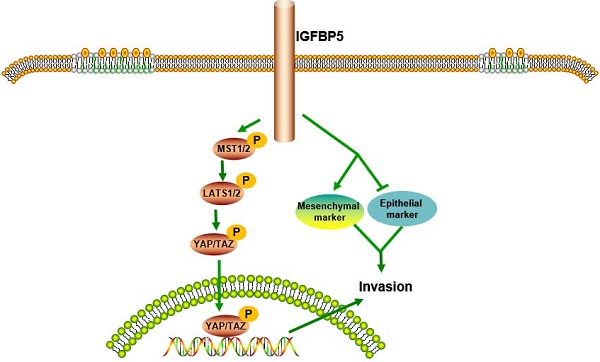
Results: IGFBP5 levels were obviously increased in glioma with higher malignancy and predicted poor outcomes by Univariate and multivariate Cox analysis. The biological function analysis revealed that IGFBP5 correlated closely with immune signatures. Moreover, IGFBP5 expression was associated with tumor infiltration of B cells, T cells, macrophages, and NK cells. IGFBP5 affected glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion probably involved in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Further study showed that IGFBP5 induced the expression of PD-L1 and CXCR4.
Conclusions: IGFBP5 as an oncogene is a useful biomarker of prognosis and correlates with progression and immune infiltration in glioma.
Keywords: Glioma, IGFBP5, Invasion, Immune infiltration, Prognostic marker

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact