3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(2):484-493. doi:10.7150/jca.90128 This issue Cite
Review
Predictive Biomarkers of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Mono- and Combination Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Organ Transplantation Center, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
2. Department of Surgery, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
3. Cell Therapy Center, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
4. Department of Pathology, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
5. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
6. Program for Cancer Biology and Drug Development, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
7. Research Center for Cancer Biology, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
Abstract
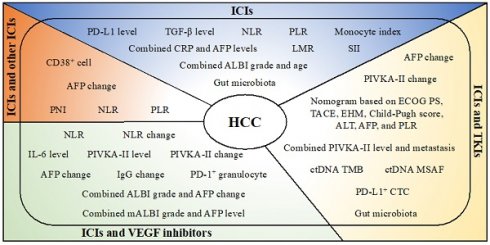
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is among the most frequent and deadly human cancers worldwide. It has been shown that interaction between immune checkpoint receptors and ligands plays a crucial role in inhibition of T cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses, thereby assisting tumor cells to evade the host immune surveillance. Therefore, several immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) that selectively block immune checkpoint receptors or ligands have been developed as clinically effective and safe immunotherapeutic agents for treating HCC, including the inhibitors targeting cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, programmed death 1, and programmed death ligand 1. In addition, various combinations of ICIs and other ICIs or tyrosine kinase inhibitors or vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors have also emerged as clinically beneficial treatments for HCC. However, the overall response rates of ICI mono-therapy and combination therapy in HCC patients remain unsatisfied, highlighting the urgent need for discovering valuable predictive biomarkers to achieve personalized therapy. This review comprehensively summarizes the literature-based evidence validating a variety of biomarkers with predictive significance for treatment responses and outcomes in HCC patients receiving various ICI-based mono- and combination therapies.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, immune checkpoint inhibitor, mono-therapy, combination therapy, predictive biomarker

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact