3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(6):1593-1602. doi:10.7150/jca.92489 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of OSCC: saliva and serum PrPC
1. Department of Stomatology, Central People's Hospital of Zhanjiang, Zhanjiang, 524037 Guangdong, China.
2. Department of Otolaryngology, Central People's Hospital of Zhanjiang, Zhanjiang, 524037 Guangdong, China.
3. Precision Clinical Laboratory, Central People's Hospital of Zhanjiang, Zhanjiang, 524037 Guangdong, China.
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage, and the high mortality of patients is mainly due to the delay of diagnosis. Cellular prion protein (PrPC) contributes to the occurrence and development of many malignant tumors. However, little has been known about the clinical and diagnostic value of PrPC in OSCC. This study investigated the levels of PrPC in the saliva and serum of patients with OSCC, OPMD and control group and their diagnostic value.
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and Clinical Proteome Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC) databases were analyzed to evaluate the expression of human prion protein gene (PRNP) mRNA and PrPC in OSCC. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) was utilized to detect the expression of PrPC in saliva and serum samples of OSCC, OPMD and control groups. Furthermore, diagnostic value and clinical significance of PrPC in OSCC was identified. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed by STRING. GO and KEGG analysis were performed by ClusterProfiler.
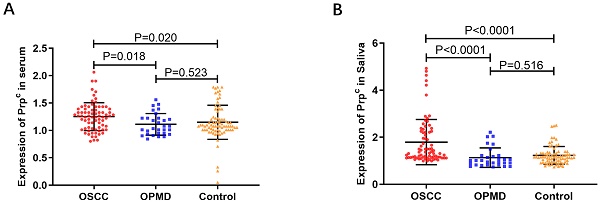
Results: The levels of PRNP mRNA and PrPC in OSCC were significantly higher than those in the control group from databases (P<0.05). Besides, salivary and serum PrPC of OSCC patients showed increased levels compared with OPMD and control groups (P<0.05). The expression of salivary and serum PrPC of OSCC was correlated with the degree of differentiation (P<0.05), and the expression of PrPC from CPTAC was related to tumor stage of OSCC (P<0.05). The areas under the diagnostic curves (AUCs) of salivary and serum PrPC were 0.807 and 0.671, respectively. GO and KEGG analysis revealed that PrPC might be related to cell adhesion, cell differentiation, signal transduction and apoptosis, and participate in the pathways of focal adhesion, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and ECM- receptor interaction in OSCC.
Conclusion: PrPC in saliva and serum may be a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of OSCC.
Keywords: Oral squamous cell carcinoma, PrPC, Saliva, Serum, Diagnosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact