3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(7):1966-1982. doi:10.7150/jca.88887 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Assessment the value of Pyroptosis-Associated Gasdermin family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Multi-Omics Comprehensive Analysis
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The First People's Hospital of Nanning, Nanning, China.
3. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China.
4. Key Laboratory of Biological Molecular Medicine Research (Guangxi Medical University), Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning, China.
*These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
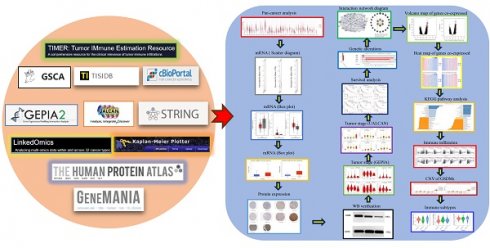
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the common primary cancers of the liver worldwide and leading cause of mortality. Gasdermins (GSDMs) family genes play an important role in the regulation of the normal physiological processes and have been implicated in multiple diseases. However, little is known about the relationship between different GSDMs proteins and HCC. The aim of this study was to explore the potential relationship between the expression, prognosis, genetic variation and immune infiltration of GSDMs family genes and HCC.
Methods: We used different bioinformatics common public databases such as GSCA, GEPIA, UALCAN, HPA, Kaplan-Meier Plotter, LinkedOmics, GeneMANIA, STRING, cBioPortal, TIMER and TISIDB to analyze the differential expression of the different GSDMs, prognostic value, genetic alterations, immune cell infiltration and their functional networks in HCC patients.
Results: All the members of the GSDMs family exhibited elevated mRNA expression levels in LIHC compared to the normal tissues, while only GSDMB, GSDMD and GSDME showed enhanced protein expression. The mRNA expression of most GSDMs members was found to be elevated in HCC patients at stages I-III (clinical stage) compared to the normal subjects. The expression of GSDMD was correlated with OS and DSS of patients, whereas GSDME was correlated with OS, DSS and RFS of patients. Gene amplification was observed to be main mode of variation in members of the GSDMs family. KEGG pathway analysis showed that genes associated with different members of the GSDMs family were enriched in the pathways of S. aureus infection, intestinal immunity, ribosome and protein assembly, oxidative phosphorylation, osteoclast differentiation and Fc gamma (γ) R-mediated phagocytosis. In addition, expression of both GSDMA and GSDME were found to be correlated most significantly with infiltration of immune cells, while GSDMA and GSDME somatic cell copy number alteration (CAN) were correlated significantly with the infiltration of immune cells. All GSDMs were noted to be associated with distinct subtypes of immune cells, except GSDMC.
Conclusions: Our findings have provided useful insights to better understand the roles and functions of GSDMs in HCC that can provide novel direction for developing therapeutic modalities for HCC, including immunotherapy.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, GSDMs, immune infiltration, Bioinformatics analysis, GSDME, Prognosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact