3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(8):2361-2372. doi:10.7150/jca.92087 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Evodiamine Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth via RTKs Mediated PI3K/AKT/p53 Signaling Pathway
1. Infectious Diseases, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, China.
2. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Regulating Metabolic Diseases Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, China.
3. Clinical School of Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work and share the first authorship.
Abstract
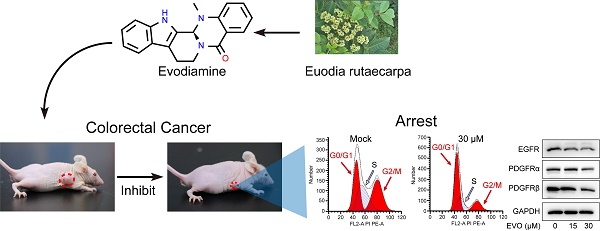
Objective: To investigate the inhibitory effect of EVO on colorectal cancer (CRC) growth and further explore the potential mechanism involving the RTKs-mediated PI3K/AKT/p53 signaling pathway.
Methods: Firstly, the inhibitory effect of EVO on CRC cells was detected in vitro by cell viability assay and colony formation assay. The effects of EVO on spatial migration and invasion capacity of cells were detected by Transwell assay. The effects of EVO on apoptosis and cycle of cells were detected by flow cytometry. Then, the molecular mechanism of EVO against CRC was revealed by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Finally, the excellent anti-tumour activity of EVO was verified by in vivo experiments.
Results: The results demonstrated that EVO exerts inhibitory effects on CRC cell proliferation, invasion, and colony formation. The cell cycle assay revealed that EVO induces G1/S phase arrest. Through RNA seq, we explored the influence of EVO on the transcriptional profile of colon cancer and observed significant activation of RTKs and the PI3K/AKT pathway, along with its downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, we observed upregulation of p53 proteins by EVO, which led to the inhibition of Bcl-2 expression and an increase in Bax expression. Consistently, EVO exhibited remarkable suppression of tumor xenograft growth in nude mice.
Conclusion: This study confirmed that EVO inhibits the proliferation of CRC cells and promotes cell apoptosis. The possible mechanism of action is inhibiting the expression of the RTK protein family, activating the PI3K/AKT/p53 apoptotic signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting Bcl-2 expression and increasing Bax expression, promoting apoptosis of CRC cells. As a natural product, EVO has very high potential application value.
Keywords: Evodiamine, Colorectal cancer, RTKs, PI3K/AKT/p53, Natural product

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact