3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(9):2646-2658. doi:10.7150/jca.94228 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Defining the biological functions and clinical significance of AKR1C3 in gastric carcinogenesis through multiomics functional analysis and immune infiltration analysis
1. Health Science Center, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315020, China.
* Authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Human aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3) is an important molecule that participates in multiple physiological metabolic processes. However, its expression, biological functions and clinical significance in gastric carcinogenesis are unclear.
Methods: We collected data from several public data portals and clinical samples and systematically analyzed the clinical significance of tissue and plasma AKR1C3 expression. Then, we filtered prognostic risk factors and established novel prognosis-related nomogram models for predicting overall survival time and postoperative recurrence risk. The application value of the nomogram models was further assessed using clinical samples. Moreover, we explored the potential biological functions of AKR1C3 in gastric carcinogenesis and metastasis through multiomics functional analysis and immune infiltration analysis.
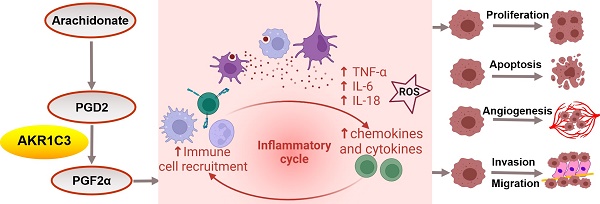
Results: AKR1C3 levels were reduced in cancer tissue but increased significantly in the plasma of GC patients; AKR1C3 expression in either sample type was closely associated with multiple clinicopathological characteristics. By combining clinicopathological factors and AKR1C3 levels, two novel nomogram models were developed to predict overall survival time and postoperative recurrence risk. Multiomics functional analysis revealed that when its expression is dysregulated, AKR1C3 can widely participate in gene expression regulation through multiple regulatory modes at the gene, RNA and protein levels and exert various crucial biological effects in carcinogenesis and metastasis. Moreover, AKR1C3 expression was correlated with the infiltration of several immune cell types, and AKR1C3 was predicted to interact with several clinical drugs.
Conclusion: Dysregulated AKR1C3 expression is related to gastric carcinogenesis and immunotherapy response and is a promising biomarker and effective biotherapy target in GC.
Keywords: AKR1C3, gastric cancer, biomarker, multiomics, immune infiltration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact