3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(8):2336-2350. doi:10.7150/jca.49138 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LINC00184 involved in the regulatory network of ANGPT2 via ceRNA mediated miR-145 inhibition in gastric cancer
1. Medical Oncology Department of Gastrointestinal cancer, Liaoning Province Cancer Hospital & Institute (Cancer Hospital of China Medical University), No. 44 Xiaoheyan Road, Dadong District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province, China 110042.
2. Gastric Cancer Department, Liaoning Province Cancer Hospital & Institute (Cancer Hospital of China Medical University), No. 44 Xiaoheyan Road, Dadong District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province, China 110042.
3. Pancreatic and Thyroid Surgery Department, Sheng Jing Hospital of China Medical University, 36 Sanhao St, Heping District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province, China 110003.
Abstract
Background: Disrupted gene levels are intimately correlated with the occurrence and prognosis of gastric cancer (GC). As genes do not function in isolation, we set out to investigate the possible relationship among mRNA and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).
Materials and methods: RNA sequencing from 406 cases of GC was acquired through the TCGA database. R packages were utilized to assess differential RNA expression. The competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network was predicted using miRcode, miRDB, mirTarBase, Target Scan and constructed by Cytoscape 3.6.1. GO enrichment analysis, KEGG pathway analysis, GSEA, and WGCNA were applied for pathway analysis. The expression of select candidate molecules was confirmed using western blot and RT-PCR in GC cells and tissues. CCK-8, EdU staining, and Transwell assays were conducted to assess the influence of candidate molecules on proliferation and invasion. The gain and loss-of-function were achieved by co-culture with sh-lncRNA, mimics and sh-mRNA. Luciferase reporters were created using the psiCHECK2 vector, and the relative luciferase activity was calculated.
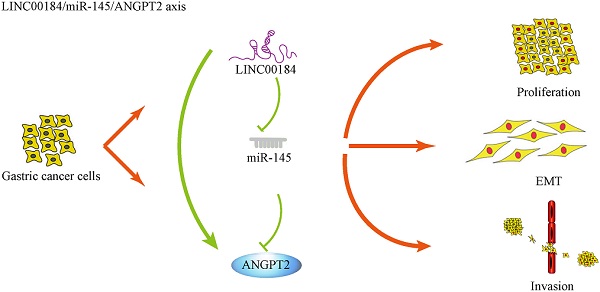
Results: Using data from TCGA, we determined differentially expressed RNAs and created a ceRNA regulatory network. Interestingly, we identified a regulatory complex surrounding ANGPT2. We detected that ANGPT2 was highly expressed in GC, which correlated with a worse prognosis. Our findings indicated that ANGPT2 encourages growth, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in GC. Importantly, miR-145 inhibits ANGPT2 and abrogates its effects. Furthermore, LINC00184, a ceRNA, blocks miR-145, thereby improving ANGPT2-mediated carcinogenesis.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the LINC00184/miR-145/ANGPT2 pathway has a crucial function in the development of GC and can act as a possible biomarker and targets for GC therapy.
Keywords: Gastric cancer, ceRNA network, TCGA, LINC00184, miR-145, ANGPT2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact