3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(11):3190-3197. doi:10.7150/jca.54429 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Serum metabolomics analysis for the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
1. Department of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan 250012, China.
2. Tumor Preventative and Therapeutic Base of Shandong Province, Feicheng People's Hospital, Feicheng 271600, China.
3. Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan 250117, China.
4. Interdisciplinary Research Center on Biology and Chemistry, and Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200032, China.
Abstract
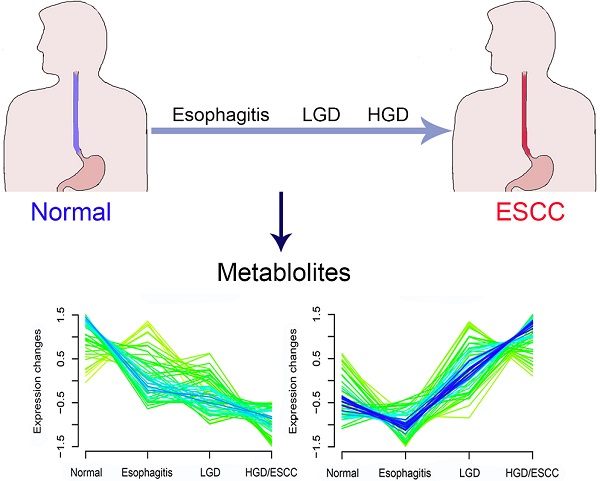
BACKGROUND: Previous metabolomics studies have found differences in metabolic characteristics between the healthy and ESCC patients. However, few of these studies concerned the whole process of the progression of ESCC. This study aims to explore serum metabolites associated with the progression of ESCC.
METHODS: Serum samples from 653 participants (305 normal, 77 esophagitis, 228 LGD, and 43 HGD/ESCC) were examined by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF/MS). Principal component analysis (PCA) was first applied to obtain an overview of the clustering trend for the multidimensional data. Fuzzy c-means (FCM) clustering was then used to screen metabolites with a changing tendency in the progression of ESCC. Univariate ordinal logistic regression analysis and multiple ordinal logistic regression analysis were applied to evaluate the association of metabolites with the risk of ESCC progression, and adjusted for age, gender, BMI, tobacco smoking, and alcohol drinking status.
RESULTS: After FCM clustering analysis, a total of 38 metabolites exhibiting changing tendency among normal, esophagitis, LGD, and HGD/ESCC patients. Final results showed 15 metabolites associated with the progression of ESCC. Ten metabolites (dopamine, L-histidine, 5-hydroxyindoleacetate, L-tryptophan, 2'-O-methylcytidine, PC (14:0/0:0), PC (O-16:1/0:0), PE (18:0/0:0), PC (16:1/0:0), PC (18:2/0:0)) were associated with decreased risk of developing ESCC. Five metabolites (hypoxanthine, inosine, carnitine (14:1), glycochenodeoxycholate, PC (P-18:0/18:3)) were associated with increased risk of developing ESCC.
CONCLUSIONS: These results demonstrated that serum metabolites are associated with the progression of ESCC. These metabolites are capable of potential biomarkers for the risk prediction and early detection of ESCC.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, serum metabolites, progression, FCM, ordinal logistic regression.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact