3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(19):5879-5887. doi:10.7150/jca.55181 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LncRNA-PANDAR regulates the progression of thyroid carcinoma by targeting miR-637/KLK4
1. Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University, Chengdu 610081, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Oncology, Daping hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, 400042, China.
3. Department of respiratory and critical care medicine, Guangyuan Central Hospital, Guangyuan City, Sichuan Province, 628000, China.
4. Department of medical oncology, Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Centre, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 610041, China.
Abstract
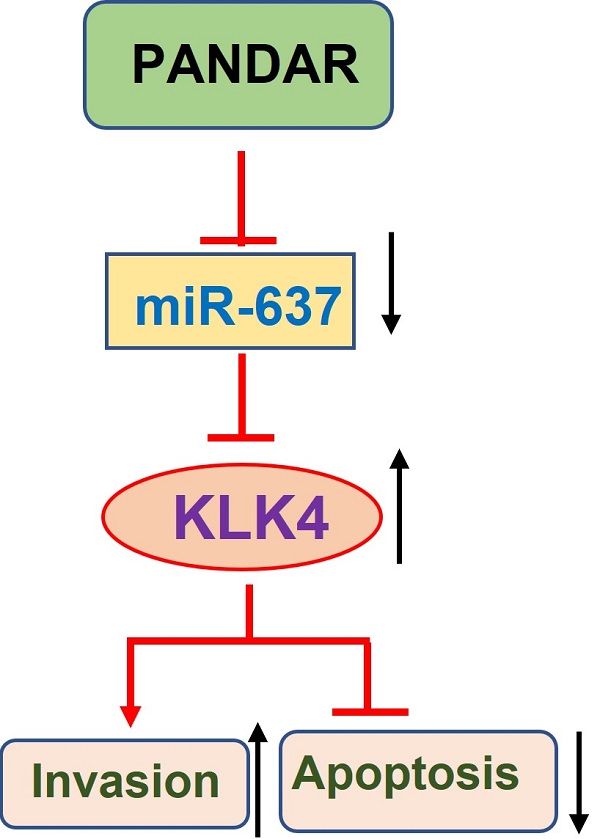
Thyroid gland carcinoma (TC) originates from follicular or parafollicular thyroid cells and is one of the most common endocrine organ malignancies. To explore the molecular mechanism by which long-chain non-coding RNAs regulate the growth and metastasis of thyroid gland carcinoma, in this study we focused on long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) that have been reported to be involved in tumorigenesis. We identified Promoter Region of CDKN 1A antisense DNA damage-activated RNA (PANDAR), which was positively correlated with thyroid gland carcinoma risk. PANDAR could promote thyroid gland carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis. PANDAR negatively correlated with miR-637, and miR-637 overexpression suppressed thyroid gland carcinoma progression, which could be reversed by PANDAR. MiR-637 could target Kallikrein-related peptidases 4 (KLK4) to inhibit its expression, which was high in thyroid gland carcinoma. KLK4 inhibited cell progression in thyroid gland carcinoma cells. Knockdown of PANDAR expression inhibited cancer progression in nude mice. Overall, PANDAR can suppress miR-637 and induce KLK4 to regulate invasion and migration in thyroid gland carcinoma. Additionally, we identified miR-637 as a target of PANDAR in thyroid gland carcinoma, and PANDAR can be used as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of thyroid gland carcinoma.
Keywords: Thyroid gland carcinoma, LncRNA PANDAR, MiR-637, KLK4, Progression

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact