3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(20):6071-6080. doi:10.7150/jca.62141 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inositol hexaphosphate sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to oxaliplatin relating inhibition of CCN2-LRP6-β-catenin-ABCG1 signaling pathway
1. Department of Nutrition, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
2. Institute of Medical Research, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, 710072, China.
3. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Xi'an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xi'an, 710061, China.
Abstract
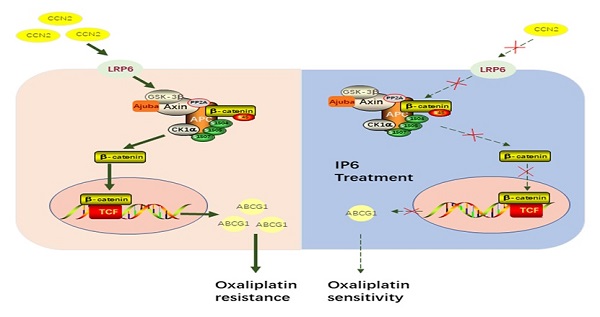
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a drastic problem in China. Oxaliplatin, a platinum-based chemotherapy drug, has limited efficacy in treating HCC, characterized by intrinsic and acquired resistance. Inositol hexaphosphate (IP6), a carbohydrate abundant in grains, has contributed to the rising popularity of whole grain products consumption for the potential protection against dozens of diseases. However, the therapeutic potential of IP6 in halting the progression of HCC remains unclear, especially in combination with oxaliplatin. The anti-proliferation and anti-migration effects of IP6 were evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The synergistic and sequential anti-proliferative effect with IP6 and oxaliplatin were also evaluated in HCC. Finally, the role of CCN2-LRP6-β-catenin-ABCG1 signaling in oxaliplatin resistance and IP6 treatment was evaluated. We proved that IP6 treatment exhibited independent anticancer effect and synergistic anti-proliferative effects in combination with oxaliplatin in HCC. Specifically, up-regulation of ABCG1 and CCN2 were associated with oxaliplatin resistance. ABCG1 was acting as a downstream molecule of the CCN2-LRP6-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in HCC cells. The IP6 treatment exhibited inhibition of CCN2-LRP6-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and downregulation of ABCG1 in HCC cells. When combined with ABCG1 knocking down in HCC cells, the anti-proliferative effect of oxaliplatin was partly impaired in combination with IP6. We suggested that IP6 treatment renders HCC sensitive to oxaliplatin and breaking the CCN2-LRP6-β-catenin-ABCG1 signaling pathway is one of the mechanism after IP6 treatment.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, inositol hexaphosphate, oxaliplatin, Wnt signaling, CCN2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact