3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(1):268-277. doi:10.7150/jca.58982 This issue Cite
Review
The functional role of Pescadillo ribosomal biogenesis factor 1 in cancer
1. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110032, China.
2. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan.
3. Cancer Center, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110032, China.
Abstract
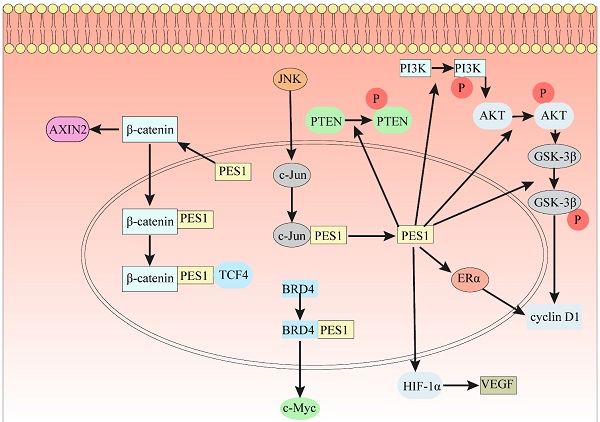
Tumors are neogrowths formed by the growth of normal cells or tissues through complex mechanisms under the influence of many factors. The occurrence and development of tumors are affected by many factors. Pescadillo ribosomal biogenesis factor 1 (PES1) has been identified as a cancer-related gene. The study of these genes may open up new avenues for early diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of tumors. As a nucleolar protein and part of the Pes1/Bop1/WDR12 (PeBoW) complex, PES1 is involved in ribosome biogenesis and DNA replication. Many studies have shown that high expression of PES1 is often closely related to the occurrence, proliferation, invasion, metastasis, prognosis and sensitivity to chemotherapeutics of various human malignant tumors through a series of molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. The molecules that regulate the expression of PES1 include microRNA (miRNA), circular RNA (circRNA), c-Jun, bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and nucleolar phosphoprotein B23. However, the detailed pathogenic mechanisms of PES1 overexpression in human malignancies remains unclear. This article summarizes the role of PES1 in the carcinogenesis, prognosis and treatment of multiple tumors, and introduces the molecular mechanisms and signal transduction pathways related to PES1.
Keywords: PES1, cancer, signaling pathway, treatment, proliferation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact