Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(3):918-931. doi:10.7150/jca.65614 This issue Cite
Research Paper
miR-17-5p promotes the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer by regulating HSPB2
1. Departments of Endoscopy Center, The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, 89 Donggang Road, Shijiazhuang, 050031 Hebei, China
2. Department of Internal medicine, The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, 89 Donggang Road, Shijiazhuang, 050031 Hebei, China
3. Hebei Medical University, 361 Zhongshan East Road, Shijiazhuang, 050017 Hebei, China
4. Department of General Surgery, Hebei Key Laboratory of Colorectal Cancer Precision Diagnosis and Treatment, The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, 89 Donggang Road, Shijiazhuang, 050031 Hebei, China
*Contributed equally
Abstract
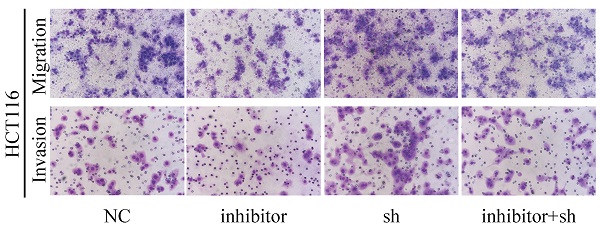
MicroRNA (miRNA) can affect tumor progression by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis. A significant upregulation of miR-17-5p expression was found in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues by miRNA microarray chip analysis. However, the underlying mechanism of miR-17-5p in CRC is still unclear. The mRNA expression of miR-17-5p was significantly higher in CRC tissues than in adjacent normal tissues. In CRC group, the expression of miR-17-5p in cancer tissues with lymph node metastasis was higher compared with those without lymph node metastasis. The biological function of miR-17-5p was demonstrated through CCK-8, colony formation, flow cytometry and transwell assays. Overexpression of miR-17-5p inhibited CRC cell apoptosis, as well as promoting proliferation, migration and invasion. Transcriptome sequencing and miRNA target prediction software suggested that HSPB2 might be a target gene of miR-17-5p and luciferase reporter detection validated for the first time that miR-17-5p binds directly to the 3'-UTR of HSPB2. In the rescue experiment, the tumor suppressive effect of HSPB2 was detected and miR-17-5p could promote cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting HSPB2. Taken together, miR-17-5p promotes invasion and migration by inhibiting HSPB2 in CRC, thereby implicating its potential as a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, microRNA, miR-17-5p, HSPB2, RNA sequencing and data analysis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact