3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(8):2515-2527. doi:10.7150/jca.67428 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A new classifier constructed with platelet features for malignant and benign pulmonary nodules based on prospective real-world data
1. Department of clinical laboratory, Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
2. Chiang Mai University College of International College of Digital Innovation, Chiang Mai, Thailand
3. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan provincial People's Hospital, Chengdu, China
4. Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
5. Radiation Oncology Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
6. State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Centre for Oral Diseases, Department of Head and Neck Oncology, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
7. Center for Informational Biology, School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
*Contributed equally
Abstract
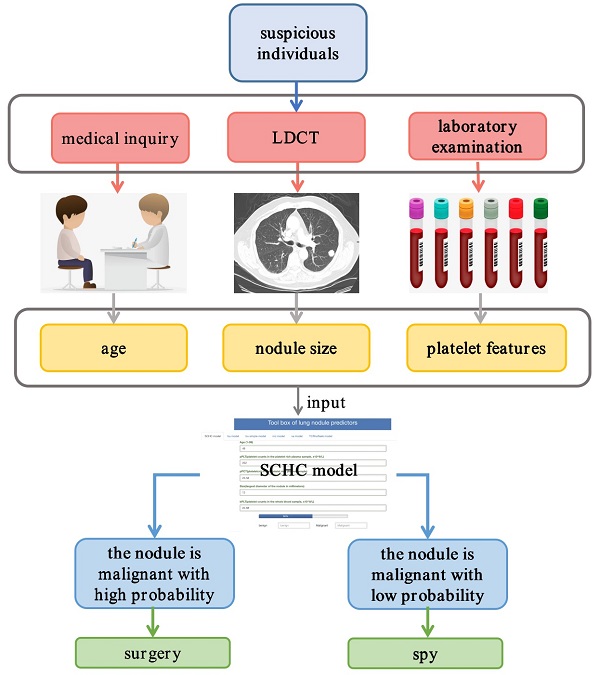
Objectives: As the pulmonary nodules were hard to be discriminated as benignancy or malignancy only based on imageology, a prospective and observational real-world research was devoted to develop and validate a predictive model for managing the diagnostic challenge.
Methods: This study started in 2018, and a predictive model was constructed using eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) based on computed tomographic, clinical, and platelet data of all the eligible patients. And the model was evaluated and compared with other common models using ROC curves, continuous net reclassification improvement (NRI), integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), and net benefit (NB). Subsequently, the model was validated in an external cohort.
Results: The development group included 419 participants, while there were 62 participants in the external validation cohort. The most accurate XGBoost model called SCHC model including age, platelet counts in platelet rich plasma samples (pPLT), plateletcrit in platelet rich plasma samples (pPCT), nodule size, and plateletcrit in whole blood samples (bPCT). In the development group, the SCHC model performed well in whole group and subgroups. Compared with VA, MC, BU model, the SCHC model had a significant improvement in reclassification as assessed by the NRI and IDI, and could bring the patients more benefits. For the external validation, the model performed not as well. The algorithm of SCHC, VA, MC, and BU model were first integrated using a web tool (
Conclusions: In this study, a platelet feature-based model could facilitate the discrimination of early-stage malignancy from benignancy patients, to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal management. This research also indicated that common laboratory results also had the potential in diagnosing cancers.
Keywords: lung cancer, pulmonary nodules, platelets, diagnosis, XGBoost, clinical laboratory

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact