3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(11):3177-3188. doi:10.7150/jca.76458 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-induced LINC00674 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating the NOX1/mTOR signaling pathway
1. The Key Laboratory of Tumor Molecular Diagnosis and Individualized Medicine of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, China.
2. Department of Pediatrics, Central Hospital of Haining, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital Haining Hospital, Haining 314400, China.
3. Graduate Department, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233030, China.
4. Department of Laboratory, Hangzhou Ninth People's Hospital, Hangzhou 310014, China.
5. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
6. Department of traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, China.
7. Department of General Surgery, Central Hospital of Haining, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital Haining Hospital, Haining 314400, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
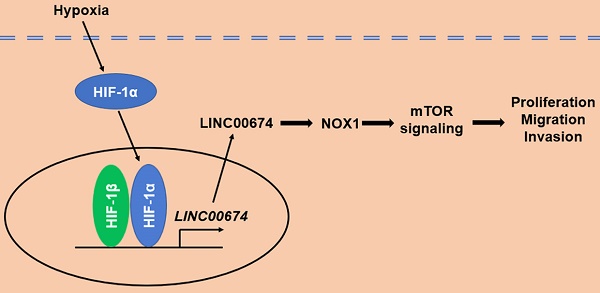
The hypoxic tumor microenvironment, a fundamental feature of solid tumors, drives hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression through regulating the transcriptional activities of protein-coding and noncoding genes. However, long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated HCC progression in hypoxic microenvironment remains largely unknown yet. In this study, we found that LINC00674 was upregulated under hypoxic conditions in a HIF-1-dependent manner, and the occupancy of HIF-1 to HRE of LINC00674 gene promoter was essential for its transcription. In addition, LINC00674 level was increased in HCC cell lines and tissues. Clinically, statistical analysis showed that LINC00674 expression was significantly associated with tumor size, venous infiltration, tumor stage and poor prognosis of HCC. Functionally, loss-of-function assays revealed that LINC00674 knockdown inhibited the migration, proliferation and invasion of HCC cells. Furthermore, LINC00674 silencing prominently repressed the mTOR signaling pathway. LINC00674 overexpression-enhanced HCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion were markedly abolished by an mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) was positively regulated by LINC00674 in HCC cells. NOX1 knockdown markedly reversed LINC00674-upregulated the p-mTOR level and HCC cells' malignant behaviors. Finally, we found that LINC00674 knockdown attenuated the growth of HCC cells in vivo. Our finding demonstrated that LINC00674 was a new HIF-1 target gene, and hypoxia-induced LINC00674 exerted a pro-proliferative and pro-metastatic role in HCC, possibly by activating the NOX1/mTOR signaling pathway. This study suggested LINC00674 as a promising therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Hypoxia, LINC00674, NOX1, mTOR pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact